REVIEWS
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the leading cause of death worldwide. According to statistics from the American Heart Association (AHA), the prevalence of CVD among young people aged 20–39 years varies: 14.2% men, 9.7% women. Behavioral risk factors for CVD, in other words those related to lifestyle, include sedentary lifestyle, smoking, alcohol consumption, unhealthy diet, overweight and obesity, and depression. These risk factors are modifiable and therefore there is great potential for reducing CVD risk through primary or secondary prevention. Young people are the most perspective group for primary prevention, since young people may be more susceptible to information influence. In addition to young people's awareness of CVD risk factors, the initial level of young people's readiness to make lifestyle changes plays a key role in reducing the risk of developing CVD.
The global prevalence of hypertension and obesity continues to rise, affecting increasingly young people. Obesity causes hypertension through a variety of mechanisms, including sympathetic nervous system activation, renin angiotensin aldosterone system, fluid and electrolyte dysregulation, inflammation, and adipokine imbalance. In turn, arterial hypertension can exacerbate obesity by altering metabolic pathways and increasing appetite. The pathophysiological features of hypertension are different between young overweight women and men. We performed a non-systematic literature review to thoroughly investigate mechanisms of pathogenetic interaction and mutual aggravation of high blood pressure and body mass index. The literature was reviewed from 2004 to the present in Russian and English using the PubMed Central, ScienceDirect, Google Scholar platforms, as well as a search in the archives of the journals Circulation and Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention using the keywords listed below.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Objective: to study the characteristics of vascular stiffness in young people, taking into account the presence of the main modifiable risk factors (FR) for the development of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Materials and methods: a survey was conducted of 38 practically healthy young people (18 boys, 20 girls) — university students, whose average age was 19.8±1.45 years. By filling in the modified diagnostic charts, the subjects assessed the presence of the main behavioral CVD disorders. Volumetric sphygmography on the VaSera-1000 device (Fukuda Denschi, Japan) was used to assess the stiffness of the main vessels and blood pressure (BP) levels in the basins of the upper and lower extremities. Results: in the examined individuals, despite their young age and the documented absence of cardio-vascular pathology, all the main cardiovascular diseases were revealed: an increased body mass index (BMI≥25 kg/m2), smoking, psychosocial factors, sedentary lifestyle, unbalanced diet, alcohol consumption, which were present in various combinations. Vascular stiffness indices — the cardio-ankle index and the biological age of the vessels — were within the normal range, while the ankle-shoulder index was reduced in 24% of the students. Conclusion: the results obtained indicate the need for primary prevention of CVD by lifestyle modification, even in young people, since the FR detected in them and the tendency to change vascular stiffness indicators can subsequently act as triggers for the early onset of diseases of the circulatory system
Objective: to evaluate the course and outcomes of ACS in patients with type 2 diabetes taking SGLT-2 inhibitors. Materials and methods: the study included patients admitted to the Research Institute – Regional Clinical Hospital No. 1 n.a. Prof. S.V. Ochapovsky” Krasnodar from 01.11.2023 to 01.02.2024. Results: a retrospective analysis of medical documentation revealed that the number of patients with ACS while taking NGLT-2 inhibitors was significantly lower compared to those taking other glucose-lowering therapy. Patients taking iNGLT-2 had a significantly lower body mass index. Significant differences concern markers of liver dysfunction and microalbuminuria, which were significantly lower in the group receiving NGLT-2. In addition, these patients were less likely to experience hospital complications such as acute kidney injury, cardiac arrhythmias, ischemic stroke, left ventricular thrombus formation, and death. Conclusions: the results of local experience with the use of iNGLT-2 in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes and ACS are presented, confirming the metabolic and cardiorenal benefits of this class of drugs in real clinical practice. In addition, the study results clearly demonstrate a more stable course of ACS and a lower risk of in-hospital complications and mortality. However, these parameters did not achieve statistically significant results due to the small sample.
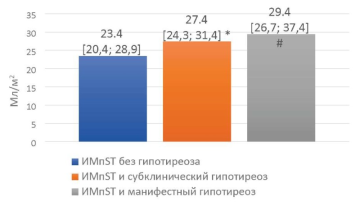
Objective: to evaluate the features of structural and functional remodeling of the left heart during hospitalization in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and concomitant newly diagnosed hypothyroidism. Materials and methods: the study included 133 patients with STEMI aged 40 to 88 years admitted to the Rostov Regional Clinical Hospital. All patients were divided into 3 groups depending on the newly diagnosed hypothyroidism: Group 1 (control) included patients with STEMI without hypothyroidism syndrome (n=57), Group 2A — patients with STEMI and subclinical hypothyroidism (n=42) and Group 2B — patients with STEMI and manifest hypothyroidism (n=34). Patient data, clinical symptoms, information on complications in the acute period of myocardial infarction, echocardiographic examination results were entered into a specially developed questionnaire. Results: patients with STEMI of all groups were found to have increased values of indexed LV ESV and LVM, decreased values of indicators characterizing myocardial contractility, as well as the presence of stage I LVDD. Patients with subclinical hypothyroidism were found to have statistically significantly higher values of the indexed LA volume than patients without hypothyroidism. The peculiarities of structural and functional remodeling of the heart in the presence of overt hypothyroidism include significantly higher linear and volumetric parameters of the LA (ILP and IOLP), a greater decrease in the contractility of the LV myocardium (lower values of SV, SI and IOC), a more pronounced impairment of diastolic properties of the myocardium (lower DT value) compared to the control group. Conclusion: in patients with STEMI and concomitant overt hypothyroidism, more pronounced remodeling of the left heart in conditions of acute myocardial injury (larger size and volume of the LA, more pronounced impairment of systolic and diastolic function of the LV).
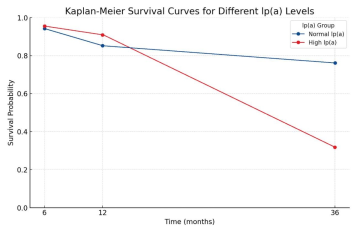
Objective: to evaluate the impact of lipoprotein (a) [Lp(a)] levels on long-term outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and single-vessel coronary artery disease. Materials and methods: the study included 110 patients diagnosed with ACS and single-vessel coronary artery disease. Patients were divided into two groups based on Lp(a) levels: Lp(a) > 50 mg/dL (n=22) and Lp(a) < 50 mg/dL (n=88). Primary outcomes included survival and the frequency of recurrent cardiovascular events at 6, 12, and 36 months. Statistical analysis included t-test, chi-square test, Kaplan-Meier method, and Cox multivariate regression. Results: at 36 months, patients with high Lp(a) levels had significantly higher rates of recurrent myocardial infarctions (50% vs. 34.1%, p < 0.001) and all-cause mortality (59.1% vs. 23.9%, p < 0.001) compared to patients with normal Lp(a) levels. Conclusion: high Lp(a) levels are a significant prognostic factor for worse long-term outcomes in patients with ACS and single-vessel coronary artery disease. Measuring Lp(a) levels may improve management strategies for these patients.
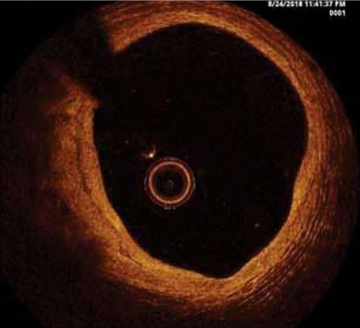
Objective: to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of implantation of everolimus-coated bioabsorbable vascular scaffolds (BSCs) based on the results of optical coherence tomography (OCT) in patients with coronary artery disease who have previously undergone percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Materials and methods: OCT data from 23 patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) were studied 10 years or more after intervention with BVS implantation. Standard criteria based on OCT analysis were used to evaluate the efficacy of BVS. The stented segment, proximal zone before the stent, and distal zone after the stent were the areas of interest. Results: in the long-term period, the structure of the artery in the area of the installed biodegradable scaffolds is a combination of fragments of an atherosclerotic plaque, a resorbed scaffold, and neointima. When visualized using coherence tomography, this structure appears as a monolayer with high signal intensity. In 42.3% of patients, structures similar to fragments of the stenting frame were visualized, but smaller in size, with a disconnected structure, without clear contours and the absence of a typical shape. In 15.4% of cases, pronounced positive remodeling of the coronary artery in the area of the installation of the bioresorbable frame was noted. Conclusions: analysis of coherence tomography data showed that the use of biodegradable frames is effective and safe, the process of degradation of the frames occurs with an increase in diameter in the stented zone and the formation of a protective monolayer, while maintaining the patency of all side branches in the implantation zone.
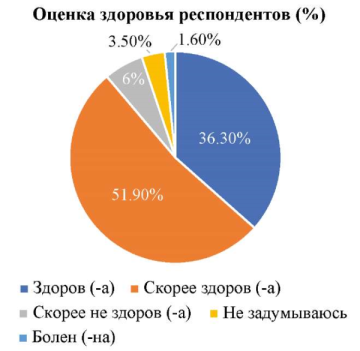
Purpose: Study of the influence and assessment of risk factors for chronic non-infectious diseases in medical students through an online survey. Materials and methods: During the period from 03/19/24 to 04/08/24, an online survey was conducted at the Rostov State Medical University using the google platform. A group of 1232 people was formed, including students from 1st to 6th year of all faculties. The results of the survey were systematized and analyzed. Results: Вy analyzing the information received from respondents, several groups of risk factors for chronic NCDs were identified: 1. Sleep disturbances; 2. Indifference to compliance with healthy eating standards; 3. Susceptibility to chronic emotional stress. Conclusion: Based on the results of the study, risk factors for chronic non-diseases were identified among Rostov State Medical University students (the leading ones were: sleep disturbance, non-compliance with healthy eating standards, stress). It was also found that indicators such as physical activity and the presence of bad habits are not common risk factors in this group of respondents. From the above, we can conclude about the feasibility and importance of introducing preventive measures to increase the importance and significance of such aspects as healthy.
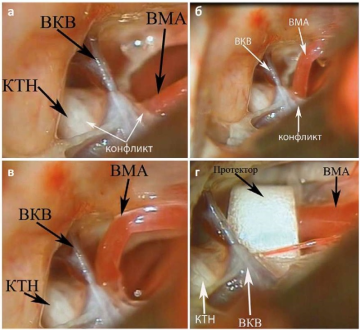
Objective: to study the long-term results of the treatment of classical trigeminal neuralgia, depending on the method of eliminating neurovascular conflict. Material and methods: the study is based on the study of long-term results of treatment of classical trigeminal neuralgia in 261 patients who underwent microvascular decompression using various techniques to eliminate neurovascular conflict by processing archival medical histories, results of outpatient examinations and telephone interviews of patients. Results: the best long-term results were in patients for whom the elimination of neurovascular conflict was performed by moving the loop of the conflicting artery to a conflict-free position with its confinement in a muff-like microprotector. Conclusion: Prevention of the resumption of neurovascular conflict in the postoperative long-term period by enclosing the conflicting artery in a microprotector moved to a conflict-free position provides the best long-term results with less colic of the disease.
Objective: to identify the clinical features of atypical forms of CIDP, improve the diagnosis of this nosology at the outpatient stage by objectifying the reference points in the clinical picture and focusing the attention of primary care specialists on this pathology. Materials and methods: the medical records of 203 patients admitted to the neurological center of the Rostov State Medical University in the period from January 1, 2014 to April 1, 2024 with a diagnosis of polyneuropathy were analyzed. The examination included a general clinical and neurological examination, an electrophysiological study (stimulated electroneuromyography on the Natus Keypoint Focos neurophysiological complex), as well as laboratory evaluation of blood and cerebrospinal fluid tests. Results: to objectify the speed of diagnosis, the “debut-diagnosis” interval was calculated. In patients with the motor form of CIDP it averaged 2.2 years, in patients with the sensory form of CIDP it was 3.9 years. In the group of patients with a typical clinical picture of CIDP, this indicator ranged from 1.5 to 4.5 years. Conclusions: CIDP is a rare acquired neuropathy of dysimmune origin, heterogeneous in course and clinical manifestations, but classified as curable. The variety of forms of the disease and its course cause difficulties in timely diagnosis and initiation of pathogenetic therapy. While early diagnosis and initiation of therapy significantly improve the prognosis for this category of patients.
CLINICAL CASES
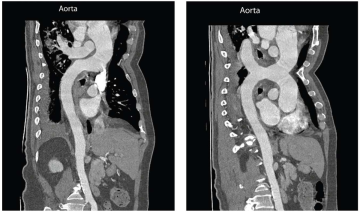
The descriptions of two cases of aortic dissection with an atypical picture, erroneously regarded as a pulmonary pathology, are presented. A thorough analysis of the clinical picture and the timely use of imaging diagnostic methods made it possible to establish the correct diagnosis and select presented.
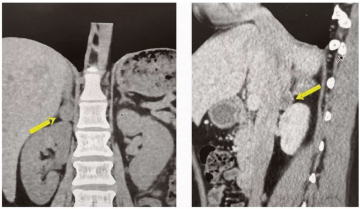
The article considers the most common causes of renal artery patency, diagnostic process algorithms and differential diagnosis for renal artery stenosis at different ages. The first significant clinical manifestation of renal artery stenosis of various etiologies is arterial hypertension (AH). It is poorly controlled AH, including resistant AH, developing at a young age, that is the basis for the diagnostic search for secondary causes of high blood pressure, including narrowing of the renal arteries. The article presents a clinical case of uncontrolled AH in a young man. A comprehensive assessment of clinical manifestations, laboratory and instrumental examination results made it possible to diagnose unilateral renal artery stenosis of atherosclerotic genesis.
The article is devoted to the clinical observation of a patient with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome 2A, characterized by a combination of pheochromocytoma, medullary thyroid cancer and hyperplasia of the parathyroid glands. The features of diagnostics of this disease, preoperative preparation, as well as principles of observation for several years after surgical treatment are described. In addition, data on the features of diagnostic search and tactics of management of family members with this syndrome are provided.
LECTURES
Serum ferritin (SF) is typically present in serum at concentrations directly related to iron (Fe) storage and is therefore traditionally used as an indicator of Fe levels in body tissues. Reducing its level is the “gold standard” for diagnosing widespread iron deficiency conditions. No less significant is hyperferritinemia — a nonspecific syndrome that occurs when Fe reserves are overloaded, a number of immunoinflammatory, infectious, oncological diseases, liver diseases, etc. In many pathological conditions, the level of SF determines the severity and prognosis of the disease. Ferritin concentrations greater than 1000 ng/mL, regardless of cause, have been shown to be associated with higher mortality. The reason for the increase in the level of SF in liver pathologies (cancer, hepatitis, cirrhosis) is associated with the process of its release from hepatocytes during their destruction. On the other hand, excessive synthesis and/or cellular secretion of ferritin occurs under the influence of various stimuli (cytokines, oxidative stress, hypoxia, oncogenes and growth factors). The interpretation of elevated ferritin values goes far beyond the role of an indicator of replenishment of Fe stores in tissues. Only 10% of cases of hyperferritinemia are associated with iron overload; in most patients, it is defined as the result of the acute phase and a reactive increase in ferritin levels against the background of any disease. The variety of symptoms of iron deficiency syndromes and hyperferritinemia is due to the involvement of many organs and systems, which requires a thorough examination (study of complaints, anamnesis, family and concomitant diseases, as well as the necessary laboratory and instrumental studies) to search for possible causes. Systemic Fe homeostasis must be closely monitored on a regular basis. It is required to comply with the conditions for blood sampling for SF. Reference values for SF concentrations vary depending on the analytical methods used and the population studied. Age and gender play an important role. Given the range of reference values, it is important for a particular patient to focus on the initial level of his ferritin, determined against the background of health and well-being during clinical observation.
EXPERIENCE EXCHANGE
The article discusses a morning conference in a multidisciplinary therapeutic hospital as one of the effective and concentrated forms of professional education and the formation of clinical thinking among young specialists. The department's staff members' own experience of conducting morning conferences at a multidisciplinary hospital is presented. Among the many functions of the morning conference, emphasis was placed on the educational role in the process of training clinical residents and senior medical students. The role of duty was discussed with the presentation of the results at the morning conference, the possibility of analyzing lethal outcomes, clinical and anatomical comparison, and deontological aspects.