REVIEWS
Hemostatic disorders in COVID-19 play an important role in the pathogenesis and clinical implications of the disease. The ability to identify factors and risk of developing thrombotic complications, to interpret the peripheral blood and coagulation dynamics, knowledge of diagnostic criteria possible of hemostatic disorders (DIC, sepsis-induced coagulopathy, antiphospholipid, hemophagocytic, hypercoagulation syndromes, etc.) are necessary to determine the scope of the survey, differentiated prescription of adequate therapy (including anticoagulants, blood components, plasmapheresis), which determines a greater efficiency of complex treatment and prognosis of patients with COVID-19.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
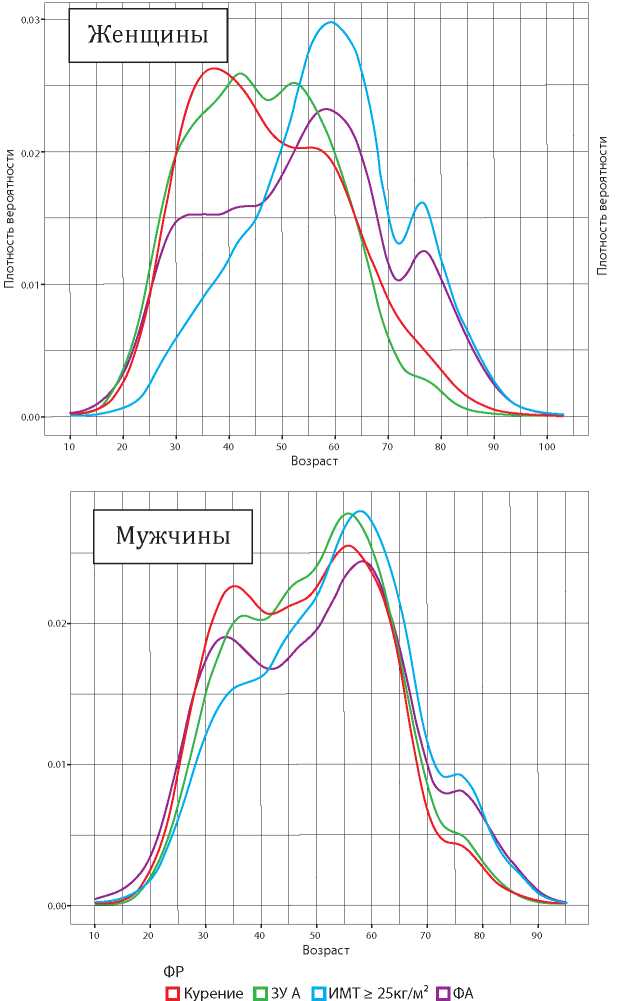
Objective: to estimate the prevalence in the dynamic of physical inactivity, overweight and obesity, smoking and alcohol abuse in a representative sample of the European part of the Russian Federation.
Materials and methods: the population of eight subjects of the European part of Russia was randomized in 2002. The resulting sample was examined by local doctors. The resulting sample included 19,503 respondents who were examined by local doctors in 2002 and 2017.
Results: from 2002 to 2017 the prevalence of smoking has decreased from 23,1 to 20,5% (р < 0,001) (47,9 – 42,6% (р < 0,001) among men and 4,8 – 4,5% (р = 0,323 among women)). The smoking index among men has decreased from 18,8 to 17,8 (р = 0,024) and from women increased from 7,7 to 10,6, р < 0,001. The prevalence of alcohol abuse has decreased from 32,2 to 22,3% (р < 0,001) (51,6 – 39,0% (р < 0,001) among men and 17,4 – 10,1% (р < 0,001) among women). Average dose of ethanol, among drinkers has changed from 84,0 ± 94,4 ml to 75,4 ± 75,5 ml (р < 0,001) (120,6 ± 111,9 – 97,7 ± 85,2 (р < 0,001) among men and 44,7 ± 45,3 – 46,0 ± 46,3 (р < 0,001) among women). Percentage of respondents who are overweight or obese has increased from 46,9 to 60,0% (р < 0,001) (41,6 – 58,2% (р < 0,001) among men and 50,9 – 31,3% (р < 0,001) among women). Although the prevalence of inactivity has decreased from 83,2 to 81,0% (р < 0,001) (79,8 – 78,4% р = 0,045 among men and 85,7 – 83,0% (р < 0,001) among women), the proportion of people without physical activity has increased from 71,5 to 74,0% (р < 0,001), because the proportion of people with low physical activity has decreased.
Conclusion: the prevalence of bad habits in Russia is decreasing, but the proportion of people who have inactivity, overweight and obesity is increasing. These facts will not significantly reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in Russsia, and require optimization of population prevention programs that will reduce the prevalence of inactivity, overweight and obesity in society.
Objective: to assess endothelial dysfunction and its genetic and immunological mechanisms in patients with refractory arterial hypertension.
Materials and Methods: at this study 42 patients (30 men (71.4%) and 12 women (28.6%)) with refractory arterial hypertension of III severity were examined. The patient's average age was 59.4 ± 1.12 years. The metabolic stability of the endothelium was assessed by a pharmacological test for endothelium-dependent vasodilation. Immunological analysis was carried out by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Genetic testing was performed on genomic DNA taken from whole venous blood samples.
Results: in 33.3% of cases, a loss of metabolic resistance of endothelial cells to oxidative stress products was recorded. An imbalance was revealed between cytokines of a pro-inflammatory nature (tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6)) and anti-inflammatory substrates (interleukin-4, interferon-γ) in favor of the former. In patients with refractory arterial hypertension, a decrease in metabolic endothelial resistance is associated with the presence of «-174 G/C» polymorphism in the IL-6 gene and «308 G/A» in the TNF-α gene.
Conclusions: in 1/3 of the examined patients with refractory arterial hypertension, there was a loss of endothelial cell resistance to the action of cytotoxic products, associated with hyperproduction of TNF-α, IL-6, as well as the presence of polymorphism «-174 G/C» in the IL-6 gene and «308 G/A» in the TNF-α gene.
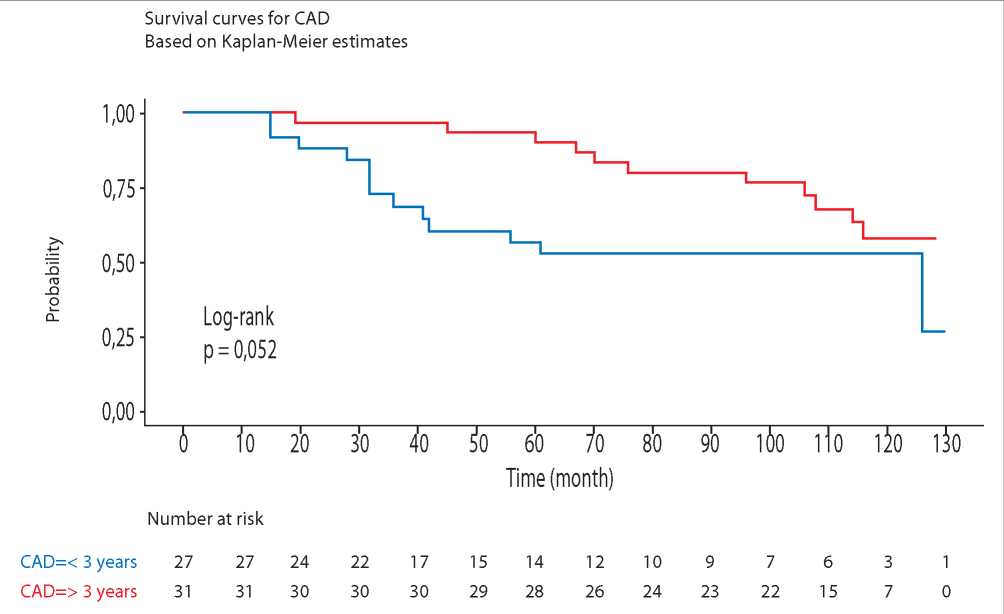
Objective: to conduct a comparative analysis of survival rate and development of heart transplant coronary artery disease risk factors during early and late post-transplantation periods.
Materials and methods: a retrospective analysis of 58 patients with was conducted in S.V. Ochapovsky Region Clinical Hospital № 1, Krasnodar. Inclusion criteria were patients with vasculopathy; group № 1 — recipients with heart transplant coronary artery disease up until 3 years after heart transplantation; group № 1 — recipients with heart transplant coronary artery desease 3 years after heart transplantation. Endomyocardial biopsy, coronary angiography and immunological examination were used for monitoring heart recipients.
Results: survival rate in group № 1 — 51,9%; in group № 2 — 64,5%. During studying the influence of age category on survival rate it was discovered that belonging to the age category influences on the survival rate in group № 1, p – 0,023. Death risk in group №1 is 1,7 (0,59 – 4,85) times higher in comparison with group № 2. When combined heart transplant coronary artery desease with cellular and humoral rejection in group №1 death risk is reliably 2,75 (1,58 – 4,78) times higher (p = 0,010). The frequency of heart transplant coronary artery desease recurrence does not have a meaningful impact on the survival rate of the recipients with heart transplant coronary artery desease n both groups. One of the meaningful risk factors in two groups, which affects heart transplant coronary artery desease development is cytomegalovirus infection. Cellular rejection is also a fact which influences lethal outcome.
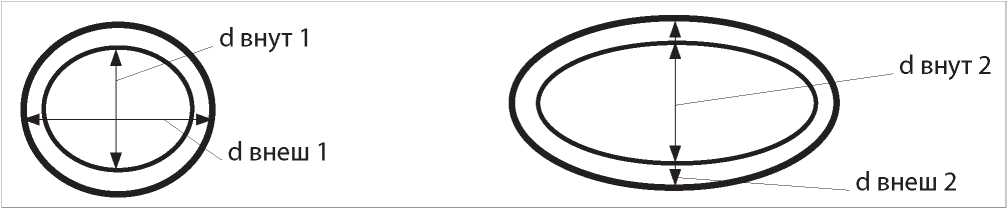
Objective: to determine the significance of clinical, laboratory and morphometric indicators of structural restructuring of kidney tissue in the prognosis of remodeling of small-diameter kidney arteries in patients with primary chronic glomerulonephritis.
Materials and methods: the study included 97 patients with primary chronic glomerulonephritis and indications for puncture nephrobiopsy. In all patients, anamnestic and clinical and laboratory risk factors were recorded, and nephrobiopsy was performed. When performing morphometric analysis of nephrobiopsy, the state of the tissue and vessels of the kidneys of small diameter was studied. To achieve this goal, all patients were divided into two groups, the ranking of which was carried out according to the median wall thickness of the interlobular artery.
Results: Among all the risk factors studied, a statistically significant effect of an increase in the stages of hypertension (χ2 criterion = 4.24, p = 0.03) and a decrease in GFR (χ2 criterion = 5.92, p = 0.015) on the risk of increasing the thickness of the interlobular artery was found. The indicators of structural reconstruction of the renal tissue did not have a statistically significant effect on the likelihood of remodeling of the arterial wall. However, a direct correlation of weak strength was found between the severity of tubulointerstitial inflammation and the thickness of the wall of the interlobular artery (r = 0.23, p = 0.02).
Conclusions: this work shows the paramount importance of hypertension, accompanied by damage to target organs, as a marker of remodeling of the vascular wall of the interlobular artery in patients with chronic glomerulonephritis.
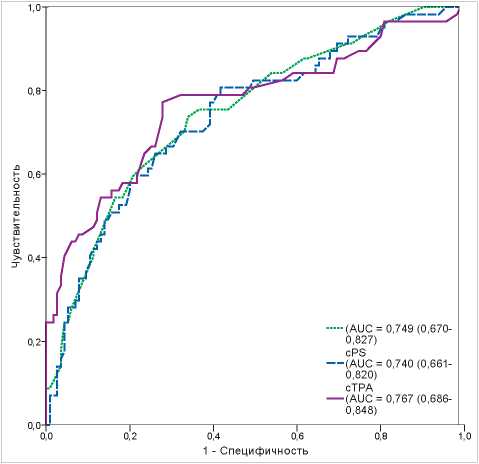
Objective: to examine the prognostic value of ultrasound markers of carotid atherosclerosis in relation to the presence of asymptomatic lower extremity peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Materials and Methods: the study included 193 patients with carotid atherosclerosis. All patients underwent duplex ultrasound scanning (DUS) of carotid and lower limb arteries. The carotid plaque score (cPS) was determined as the total height of all plaques in the carotid arteries. The carotid total plaque area (cTPA) was estimated in the longitudinal position, the area of plaque was measured in the manual trace mode.
Results: asymptomatic lower extremity PAD was diagnosed in 31.6% of patients. The increase in cTPA, in contrast to cPS and the degree of carotid stenosis, was independent predictor of lower extremity PAD and was associated with an increase in the relative risk of its presence by 6.78 times (95% CI 2.48-18.5; p <0.0001). cTPA ≥42.5 mm2 made it possible to diagnose asymptomatic lower extremity PAD with a sensitivity of 70.2% and specificity of 73.0%.
Conclusion: In patients with carotid atherosclerosis among carotid atherosclerosis markers only cTPA, in contrast to cPS and the degree of carotid stenosis, had an independent predictive value regarding the presence of asymptomatic lower extremity PAD.
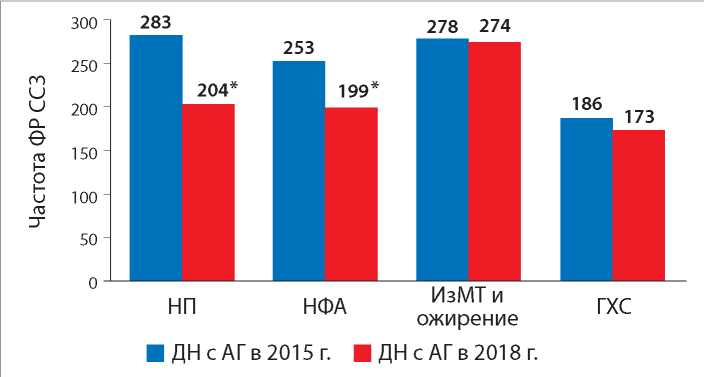
Objective: to study the dynamics of risk factors for cardiovascular diseases in patients who are under dispensary observation for the main disease arterial hypertension and coronary heart disease; the frequency of visits to a medical organization, depending on the status of dispensary observation in a cohort of adults in 2015 and 2018.
Materials and Methods: on the basis of the outpatient department of the Scientific Research Institute – Krasnodar Regional Hospital No. 1, we analyzed the incidence of CVD in the adult cohort (n = 1170), which passed of the clinical examination twice in 2015 and 2018. The analysis was carried out in groups depending on the status of the dispensary observation («not on dispensary observation», «total on dispensary observation» and «consisting on dispensary observation with CVD»).
Results: a decrease in unhealthy diet by 32.21%, 28.78% and 28%, respectively, was shown in the groups «not on dispensary observation», «total on dispensary observation» and «consisting on dispensary observation with CVD» in 2015 and 2018, (χ2 = 80.45, p = 0.001, χ2 = 59.96, p = 0.001 and χ2 = 47.8; p = 0.001). In the groups «not on dispensary observation», «total on dispensary observation» and «consisting on dispensary observation with CVD» in 2015 and 2018, there was a decrease in low physical activity by 50.33%, 24.72% and 21.85%, respectively (χ2 = 79.16, p = 0.001, χ2 = 30.6, p = 0.001 and χ2 = 22.42; p = 0.001). Against the background of the ongoing preventive measures in 2015 – 2018. the cohort showed an increase in overweight and obesity by 19.2% in the «not on dispensary observation» group (χ2 = 4.84, p = 0.028); an increase in the frequency of elevated blood pressure by 48.33% in the «not on dispensary observation» group and a decrease in its frequency in the «consisting on dispensary observation with CVD» by 24% (χ2 = 19.77, p = 0.001, χ2 = 7.1; p = 0.008). Against the background of the ongoing preventive measures from 2015 to 2018, a tendency to reduce the frequency of FR CVD was revealed. A significant decrease in unhealthy diet (p = 0.001), low physical activity (p = 0.001), was registered in individuals who were on dispensary observation according to the main nosology of hypertension. In the group of individuals who were on dispensary observation according to the main nosology, there was a significant decrease in unhealthy diet (p = 0.006) and low physical activity (p = 0.023). In patients who are on dispensary observation with CVD, there was a favorable dynamics in terms of achieving the target values of the level of blood pressure and cholesterol. The revealed tendency to decrease the frequency of visits due to CVD in patients «consisting on dispensary observation» by 32.2%, including» consisting on dispensary observation with CVD» by 33.8% for the period 2015 – 2018.
Conclusions: there was a tendency to decrease the frequency of risk factor CVD and the frequency of visits due to CVD in patients «consisting on dispensary observation», which indicates the effectiveness of measures carried out within the observation, regardless of the nosological group of patients.
Objective: to assess cerebral blood flow and reveal early myocardial remodeling in COPD patients with varying degrees of airflow restriction.
Materials and methods: the research included 105 patients with COPD from 1 to 4 degrees of severity, depending on the degree of restriction of FEV1 without CVD, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, obesity, other systemic and oncological diseases. Average age was 57.12 ± 0.68 years, men 45%. 5 groups were identified: mild severity of COPD (GOLD1, = 24), moderate (COLD2, n = 39), severe (GOLD3, n = 30), very severe (GOLD4, n = 12). Control group (n = 37) was tobacco free and CVD. Blood pressure and ultrasound tracranial dopplerography were performed in all groups. Transtoral echocardiography with assessment of global and local LV longitudinal deformation by the strain method and determination of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (DDLV) was performed in GOLD1 and GOLD2 groups. Parameters of average values of deformation in basal, medial and apical segments are evaluated. Results were processed with Microsoft Excel 2016 and STATISTICA 10 (StatSoft, Inc., USA).
Results: arterial hypertension (AH) was detected in 56.4% of patients in the COLD2 group; 56.7% of patients in the GOLD3 group and 100% of patients in the GOLD4. Сhanges in cerebral blood flow were not found in the GOLD1-3 groups. Significant increase of linear blood flow rate of middle cerebral arteries and index of peripheral vascular resistance were detected in group GOLD4 relative to control and GOLD1-3 groups (p < 0.05). DDLV of 1 type was revealed in 27.7% of patients of COPD and was higher at patients with COPD and AH - 62.5% (χ²=11.5, р =0.009). Pathological patterns were identified at the level of the basal and medial parts of the left ventricle in patients with COPD.
Conclusion: preclinical signs of target organ involvement identified in COPD patients without cardiovascular disease. Changes in cerebral blood flow in the form of an increase in linear blood flow rate and peripheral vascular resistance index were detected in the GOLD4 group. DDLV of 1 type was detected in the GOLD1-2 groups and was found more frequently in the combination of COPD with AH. Pathological patterns were identified at the basal and medial left ventricular levels in a combination of COPD and AH. Changes in target organs indicate the need for an in-depth search to reclassify cardiovascular risk and identify an individual prevention plan.
Objective: to describe the clinical and epidemiological features of idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating diseases and to determine the factors influencing their course.
Materials and methods: the study included 803 patients with idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating diseases using patient questionnaires and scales, laboratory and instrumental research methods. Statistical processing of the results was carried out using a point biserial coefficient and programs for analyzing large data arrays and machine learning.
Results: a dynamic increase in the prevalence of some forms of idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating diseases was revealed, the difficulties of differential diagnosis of rare forms of demyelination and the need to create a unified version of their classification are reflected. In the studied population, the effectiveness of liquorological examination in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis in the early stages of the disease was shown. It has been shown that the likelihood of developing highly active multiple sclerosis is influenced by both a genetic factor and concomitant inflammatory, allergic and autoimmune diseases, surgical interventions, dietary habits, childhood infections, and a history of pregnancy.
Conclusions: given the complexity of the differential diagnosis of idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating diseases and the appointment of modifying therapy in multiple sclerosis in the early stages, it is necessary to create a combined classification and maintain a common register.
CLINICAL CASES
Primary exudative enteropathy is a rare disease caused by the formation of lymphatic vessel abnormalities in the intestinal wall, the development of pathological lymph flow into the intestinal lumen, and increased loss of plasma proteins in the feces. The leading clinical syndrome of the disease is edema with the development of hypoalbuminemia and dysproteinemia. To establish the diagnosis, it took numerous studies with the exception of the patient’s pathology of the kidneys, liver, and inflammatory bowel diseases. The course of the disease was characterized by significant resistance to therapy.
Presented are three clinical observations of patients with a rare, but one of the oldest, genetic disease, which according to modern concepts belongs to the group of autoinflammatory diseases — familial Mediterranean fever. In the cases described, the diagnosis was first made in adulthood. The main purpose of the description of these cases is to draw the attention of practitioners to the possibility of early diagnosis and adequate pathogenetic therapy of this cohort of patients with an ethnic predisposition, but manifested regardless of the place of modern residence.
Presented are three clinical observations of patients with a rare, but one of the oldest, genetic disease, which according to modern concepts belongs to the group of autoinflammatory diseases — familial Mediterranean fever. In the cases described, the diagnosis was first made in adulthood. The main purpose of the description of these cases is to draw the attention of practitioners to the possibility of early diagnosis and adequate pathogenetic therapy of this cohort of patients with an ethnic predisposition, but manifested regardless of the place of modern residence.
EXPERT OPINION
At online scientific expert meeting of the South region held on October 3, 2020, the results of the international multicenter study EMPEROR-Reduced were discussed. Number of proposals and recommendations were adopted for the further study of the cardiovascular and renal effects of empagliflozin, its use in clinical practice in patients with chronic heart failure.