REVIEWS
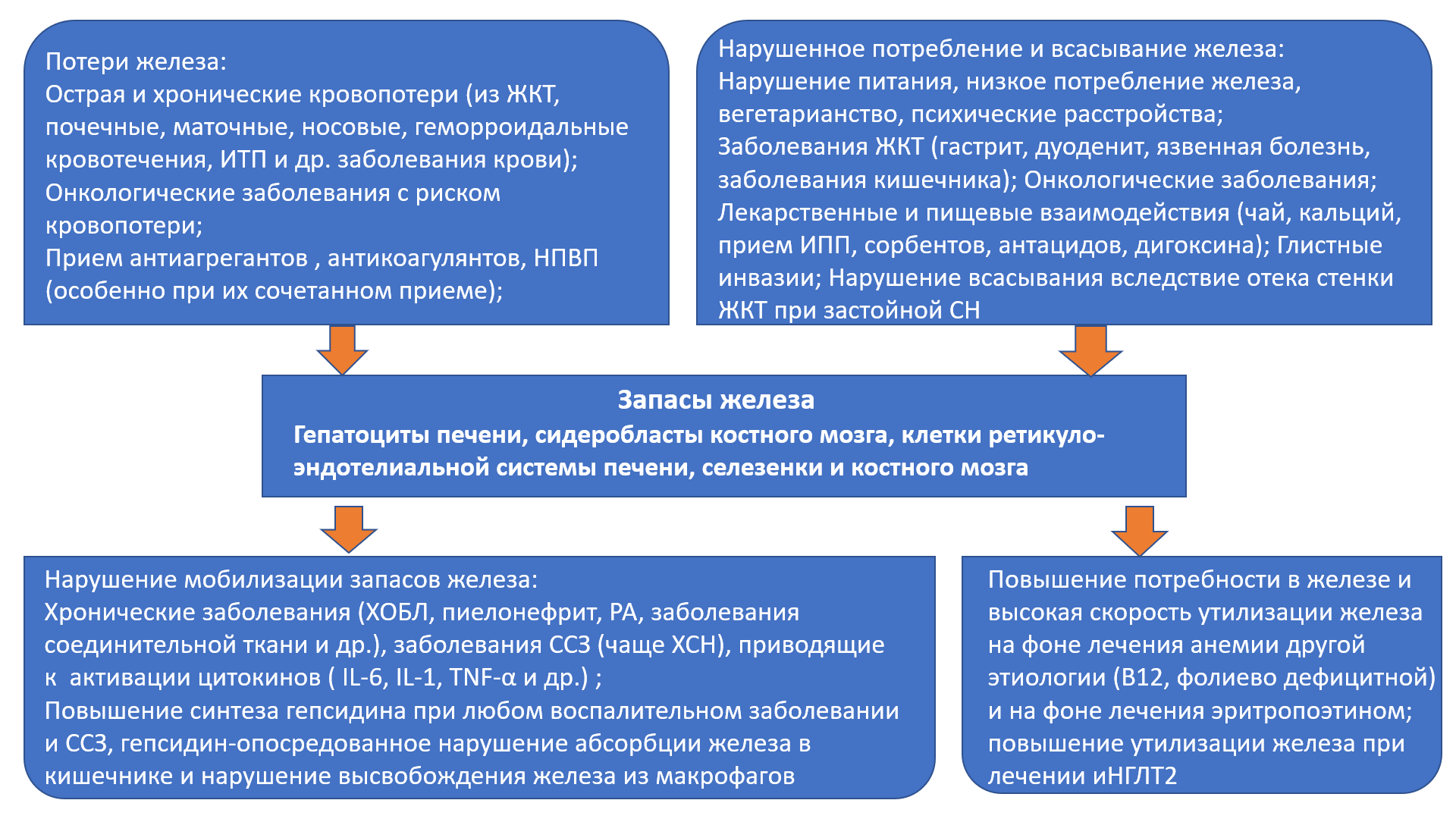
The article discusses the problem of comorbidity of iron deficiency conditions and cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Iron deficiency conditions (latent iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia) significantly increase the risk of developing and progressing CVD. A number of studies have found that, regardless of the presence or absence of anemia, iron deficiency leads to the development of cardiovascular complications, a worsening of quality of life and an increase in mortality in patients with CVD. Currently, the most studied is the effect of iron deficiency on the prognosis of patients with chronic heart failure (CHF). The article discusses the etiology and pathogenesis of the development of iron deficiency in CHF, the mechanisms of the adverse effect of this condition on the quality of life, functional status, and life prognosis. The article presents an analysis of clinical studies on the treatment of iron deficiency conditions in CHF and excerpts from current clinical guidelines. Data are presented that describe the contribution of drugs for the treatment of CHF (guideline directed therapy) to the correction of anemia and iron deficiency. The article discusses the impact of iron deficiency conditions on the course and prognosis of life in atrial fibrillation (AF) and coronary heart disease (CHD). The negative contribution of iron deficiency states to the development of exacerbations of CVD, an increase in the number of hospitalizations and an increase in the risk of death in these categories of patients is emphasized. Despite the known negative impact of iron deficiency conditions on the functional status and prognosis of patients with CVD, there is still insufficient data on the efficacy and safety of iron deficiency correction in patients with CVD.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the strongest independent risk factors for the development of atrial fibrillation (AF). Their combination is increasingly common, creating a high risk of complications and poor outcome in patients. A search and analysis of 8907 literature sources from the Scopus, Web of Science, PubMed/MedLine, The CochraneLibrary databases was carried out for the keywords "diabetes mellitus", "atrial fibrillation", "glycemic control", "hypoglycemic therapy". The review presents current ideas about the mechanisms underlying the development of AF in DM, as well as the effect of certain classes of hypoglycemic and other drugs on the risk of AF, some features of the treatment of AF in combination with DM.
The first human cases of new coronavirus (COVID-19), for the disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), were in Wuhan, in December 2019. By June 2022 there had been more than 500 million with confirmed cases of new coronavirus and over 5 million lives lost to the disease. During the earlier SARS-CoV-1 and MERSCoV epidemics, patients often developed bacterial coinfections and had a higher mortality rate. The aim of this work is to summarize the results of a study of the frequency and nature of bacterial infection in patients with COVID-19. Various studies was been in USA and countries of Asia and Europe show conflicting results regarding the prevalence of secondary bacterial infections in patients with COVID-19, from 1% to 50%. Bacterial co-infection is relatively infrequent in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Risk factors of bacterial infections in patients with COVID-19 are more 60 years old, prolonged hospital length of stay, reanimation unit admission (severe disease COVID-19), chronic bacterial infection in anamnesis, immunosuppression therapy. The most common bacterial microorganisms identified in patients with infection of the lower respiratory tract, who hospital length of stay less than 48 hours are Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae. In patients, who hospital length of stay more than 48 hours the main pathogens are P. aeruginosa, Klebsiella spp., S. aureus. The data obtained indicate a low frequency of bacterial infections in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. Early infections are quite rare, more often bacterial infections are secondary and develop after 48 hours of the patient's stay in the hospital. The causative agents of early and late infections are different. Most often, an infection of the respiratory tract is noted, less often — the urinary system and bacterial infections of other localization.
The article presents a review of the literature related to the problems of the gastrointestinal tract in gynecological practice.
Complaints from the digestive organs are interrelated with vaginal dysbiosis, a violation of the formation of the menstrual cycle. The main complaints presented by women with diseases of the female genital sphere, the causes of their occurrence and measures to eliminate these complaints are considered.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
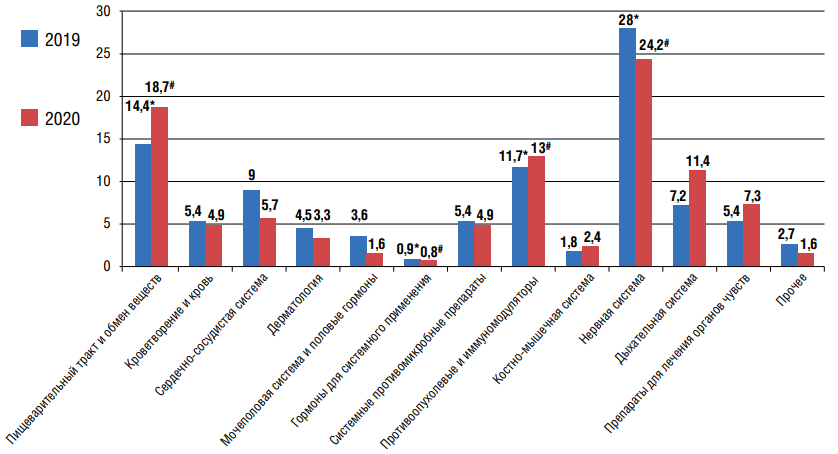
Objective: using the example of data for 2019–2020 in the Rostov region, to analyze the characteristics of spontaneous reports (SR) of adverse drug reactions (ADRs), as well as to assess their correlation with the individual characteristics of patients and the drugs used. Materials and methods: The object of a retrospective descriptive study was 234 SR about ADRs registered in the Rostov region in 2019-2020. Results: highest number of SR about ADRs in 2019–2020 were associated with drugs from the group "Nervous system, "Alimentary tract and inclusion metabolism" and "Antineoplastic and immunomodulators". In 2019, as well as in 2020, there was a statistically significant correlation between the indicators of the drug group and the type about ADRs, the age of the patient and the outcome of the developed ADRs. In addition, in females, a significant relationship was established between the criterion for the severity about ADRs and its outcome. Conclusions: the results obtained during the implementation of this study include the identification of common values and prerequisites for the development about ADRs in 2019 and 2020, and therefore can be taken into account when assessing a risk-based algorithm for the exclusion and emergency of identifying ADRs. This, in turn, inevitably constitutes and personalizes the choice of pharmacotherapy, balanced in terms of "efficacy-safety".
Aim. The aim of the work was to study for three years the dynamics of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in patients with comorbid pathology who had suffered a myocardial infarction with ST segment elevation. Materials and methods. The study included patients of both sexes older than 18 years. All of them signed an informed consent for participation in the study. The inclusion criteria, in addition to signing informed consent for participation in the study, were acute myocardial infarction with ST elevation (STEMI), PCI and implantation of 1-2 stents into the left coronary artery, the presence of hypertension, type 2 diabetes melitus. Patients younger than 18 years and older than 80 years with type 1 diabetes mellitus, the presence of oncological diseases at the time of the study or in the anamnesis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic viral infections were not included. All diagnoses were established according current clinical recommendations. The patients were divided into two groups. The first group included patients with arterial hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus, the second group included patients who had suffered acute myocardial infarction with ST segment elevation, who had arterial hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Serum was used to assess the content of matrix metalloproteinase 9. A standard test kit was used ("Cloud-Clone Corp.", China) in accordance with the instructions. The calculations were carried out using Excel spreadsheets and the statistical software package Statistica 10 (StatSoftInc.) USA. Results. When studying the level of metalloproteinase 9 for 3 years in patients who had suffered a myocardial infarction, it was found that the level of MMP-9 was statistically significantly higher in patients at the time of hospitalization, then decreased by the first year after the index event and became comparable with patients who did not have MI. After 36 months from the start of the study, patients who had suffered a myocardial infarction had statistically significantly higher levels of matrix metalloproteinase 9, compared with their values by the end of the first year, however, these data are comparable to the level of MMP-9 in patients of the first group. The level of MMP-9 in the first group is comparable at all time stages of observation. Conclusion. The inflammatory marker MMP-9, under certain conditions, can serve as a good predictor for predicting fatal outcomes and repeated AMI in patients who have undergone MI.
Оbjective: to evaluate the features of daily monitoring of arterial and central aortic pressure in patients with arterial hypertension and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Materials and methods: a comparative cross-sectional study was conducted, which involved 120 patients (continuous sample, unorganized population), aged 45 to 65 years (mean age 56.2±8.8 years), including men (34 (28.3%) with AH stage I–II, 1–2 degree. The main group included 60 patients with hypertension and NAFLD, the control group included 60 patients with isolated hypertension. When examining patients, a clinical examination was carried out: taking an anamnesis, measuring "office" blood pressure, anthropometric parameters, calculating body mass index (BMI), WC. 24-hour monitoring of arterial (ABPM) and central aortic pressure (CAP) was assessed using the BPLab complex and Vasotens 24 software (LLC Petr Telegin, Russia). The SCORE scale was used to calculate total cardiovascular risk and 10-year fatal risk. Results: all patients of the study groups underwent ABPM. It was proved that in the patients of the main group, the IV SBP and IV DBP during the day and night significantly exceeded the similar parameters of patients in the comparison group (IV SBP: p=0.0019, p=0.007; IV DBP: p=0.009, p=0.009, respectively). One of the important criteria for assessing blood pressure was the determination of the degree of nighttime decrease in SBP and DBP — the daily index (SI), characterizing the balance in the work of the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system. In the main group, compared with the control group, there were more patients with SI DBP in the range from 0.0% to 10.0% (non-dipper) (p=0.034), with an increase in SBP at night (night-picker) (p=0.031). When assessing the parameters of CAP, in patients with AH and NAFLD, statistically significantly higher values of mean daily systolic (SADAo) and diastolic (DADo) aortic pressure were observed (p=0.016, p=0.039, respectively), SBP in the daytime (p=0.027), SADao and DADAO at night (p=0.002, p=0.003, respectively), compared with patients with isolated hypertension. Calculation of the risk of cardiovascular complications, in patients with hypertension and NAFLD, a significant increase in the 10-year risk of cardiovascular events was determined, compared with patients with isolated hypertension (3.7 (1.6; 6.0) vs 2.0 (0.6 ;4.3) %, p=0.013). Conclusion: according to the results of 24-hour BP monitoring, in patients with AH and NAFLD, compared with patients with isolated AH, a more significant increase in mean SBP and DBP, an increase in the rate of morning rise and BP variability, and the hypertension time index were revealed. In the main group, patients with a nocturnal increase in SBP were detected significantly more often, which indicates a greater risk of cardiovascular complications in patients with hypertension and NAFLD. In addition, compared with patients with isolated AH, patients with AH and NAFLD showed more significant increases in average daily and nighttime SBPao and DADAO.
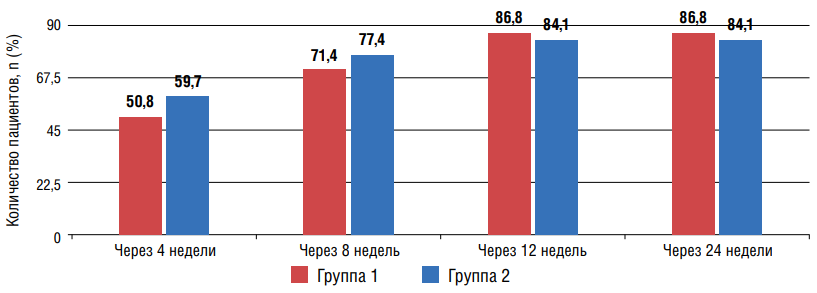
Оbjective: to compare the effectiveness of the effect of two combination therapy options on office blood pressure (BP), 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) and 24-hour BP profile (DAP) in patients with arterial hypertension (AH) associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Materials and methods: 137 patients with uncontrolled hypertension combined with DM2 and NAFLD were examined. After randomization by the "envelope" method, patients of the 1st group were assigned a combination of azilsartan medoxomil (Az-M) with amlodipine (Aml), the 2nd group a combination of olmesartan medoxomil (Ol-M) with Aml. At baseline, at 4, 8, 12, and 24 weeks, office BP was measured, and ABPM and DAP were analyzed at baseline and at 24 weeks of the study. Results: after 12 weeks in the 1st and 2nd groups, 86,8% and 84,1% of patients, respectively, reached the target level (TA) of blood pressure, which was maintained until the end of the study. After 24 weeks, both groups showed a statistically significant improvement in ABPM parameters and optimization of DAP. At the same time, taking the Ol-M/Aml combination was accompanied by more pronounced positive dynamics of some prognostically important ABPM indicators. Conclusion: despite the significant antihypertensive effect on the background of the use of both combinations, the effect on individual parameters of ABPM Ol-M/Aml was more pronounced.
Оbjective: to assess the cardiometabolic profile and cardiovascular risk factors in women with a history of hypertension during pregnancy. Materials and methods: a case-control observational study based on a prospective cohort study included 66 women, divided into two groups: group 1 — with a history of hypertension during pregnancy (n=33), and group 2 (control) — with a history of normotensive pregnancy (n=33). We applied the propensity score -matching method. Results: women in group 1 women were more often had hypertension and obesity compared with the control group. The most significant changes in the cardiometabolic profile were found in group 1: the highest concentrations of glucose and immunoreactive insulin, glycated hemoglobin, uric acid, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, C-reactive protein in serum, and HOMA-IR insulin resistance index. An increased left ventricular (LV) mass index and the urine albumin/ creatinine ratio were higher among women in group 1 compared with group 2. Conclusion: after applying the propensity score matching, the most significant differences were obtained in the frequency of hypertension, serum concentrations of alanine aminotransferase, C-reactive protein, and the frequency of elevated albumin/creatinine ratio.
Оbjective: in order to evaluate the effects (lipid-lowering, the effect on the endothelial function and oxidative stress) of pitavastatin at a dose of 4 mg in patients with dyslipidemia, arterial hypertension (AH) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) at baseline, after 4 weeks and 12 months of treatment. Material and methods: the prospective study included 33 patients (mean age 60 [54;61] years) with AH, COPD and dyslipidemia. Laboratory examination consisted in determining the lipid spectrum, the level of lipid peroxidation products, creatinine, bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase. The endothelium’s function was performed by the test with the endothelium-dependent vasodilation. We prescribed Pitavastatin (4 mg, Livazo, Recordati, Ireland) as a lipid-lowering therapy. After 12 months, the atherosclerotic plaques (AP) in the vessel was seen by the ultrasound duplex scanning of carotid arteries. Results: after 4 weeks of treatment with pitavastatin (4 mg), there was a decrease in total cholesterol — 26%, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) — 33%, triglycerides (TG) — 19%, high-density lipoprotein was increased by 18%. There was an improvement in endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress. There were no side effects in patients. Conclusion: correction of lipid metabolism disorders in AH patients with COPD by prescribing pitavastatin (4 mg) can reduce total cholesterol, LDL and TG, can positively affect endothelial function and lipid peroxidation processes. Therapy with pitavastatin (4 mg) in patients with dyslipidemia, AH and COPD is safe. It is noted the regression of AP after 12 months of regular intake of pitavastatin at a dose of 4 mg.
Оbjective: analysis of microbiocenosis of the upper respiratory tract and large intestine in patients with chronic compensated tonsillopharyngitis. Materials and methods: was carried out an analysis of a retrospective study of the microbiocenosis of the upper respiratory tract and large intestine was carried out in 126 patients with chronic compensated tonsillopharyngitis. The control group consisted of 25 apparently healthy people. To characterize the local immunity of the mucosa of the pharynx and large intestine, the content of pro-inflammatory (IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8) and anti-inflammatory (IL-4, IL-10) cytokines in the coprofiltrates of patients with chronic compensated tonsillopharyngitis was determined by enzyme immunoassay. Results: in patients with chronic compensated tonsillopharyngitis, marked disturbances were registered in the microbiocenoses of the upper respiratory tract (with a predominance of β-hemolytic streptococci and fungi Candida, recorded in 66.7% and 48.4% of patients, respectively) and the large intestine (with a moderate decrease in the content of bifidobacteria to lg 8.0 ± 0.2, lactobacilli up to lg 6.3 ± 0.15, as well as the total number of Escherichia up to lg 6.4 ± 0.2), as well as an imbalance of cytokines (a significant increase in the content of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-2, a moderate increase pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-10) and a significant (more than 15 times) increase in local synthesis of γ-interferon. Conclusions: the results of this study may indicate the translocation of microbes and their toxins into the internal environment of the body, which causes a decrease in immunoreactivity and the development of chronic systemic inflammation. These data should be taken into account in the development and comprehensive clinical and pharmacological evaluation of new drugs for the treatment of chronic compensated tonsillopharyngitis.
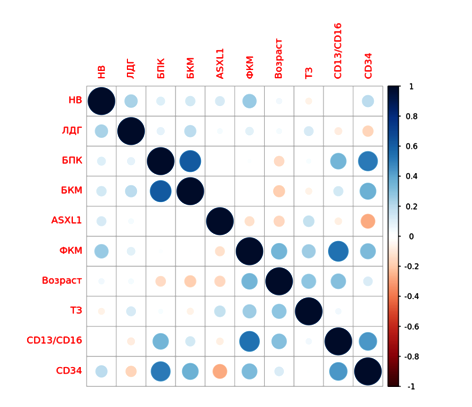
Оbjective: was to determine the prevalence of the c.1934dupG mutation in the ASXL1 gene and the R882H mutation in the DNMT3A gene in MDS and their influence on significant clinical characteristics. Materials and methods: 33 men and 17 women with a median age of 57 years (18 –83) and a verified diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome were included in the study. Twenty-two volunteers without hematologic pathology were taken as controls, of them: 8 men and 14 women aged from 22 to 65 years. PCR examination of venous blood was performed in all study groups to detect c.1934dupG and R882H with Sanger reference sequencing. Results: the R882H mutation was not detected in any of the study groups. The c.1934dupG mutation was not detected in individuals without hematologic pathology. Due to a lack of concentration of isolated DNA from venous blood cells, no analysis of amplification efficiency could be performed in 7 patients. The c.1934dupG mutation was found in 46% of patients and was found in all IPSS-R, WPSS, and MDS-CI risk groups. No differences were found in the analysis of survival in the presence and absence of the c.1934dupG mutation. Conclusions: the study demonstrated that the developed method for the detection of the c.1934dupG mutation in venous blood cells enables optimization of diagnosis. A limitation of the adapted amplification and restriction assays was the degree of blood leucopenia. No effect of the c.1934dupG mutation on the clinical course of myelodysplastic syndrome was detected.
CLINICAL CASES
Within the framework of this publication, the first description of the AFib-form of amyloidosis with kidney damage in the Russian Federation is presented. Detection of a rare form of amyloidosis became possible after morphological examination of the kidneys and typing of amyloid into AA and AL forms, as well as mass spectrometric examination of the patient's blood and urine.
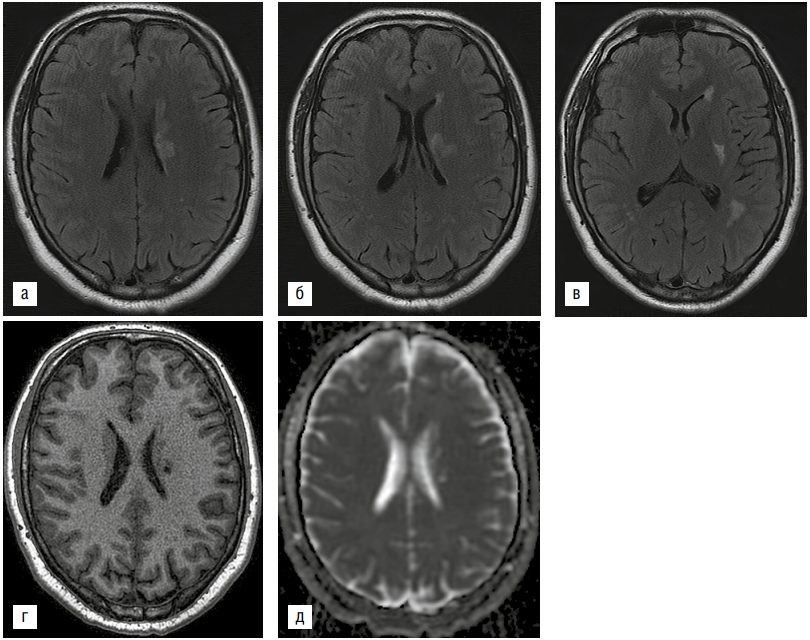
A rare case of ischemic stroke on the background of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in a 22-year-old patient is presented. The development of a stroke in this case can be associated with such factors as arterial hypertension, overweight of the patient, DIC syndrome against the background of HFRS. This observation is of interest to neurological and infectious specialists.
EXPERIENCE EXCHANGE
The article discusses the concept and educational role of the clinical conference in the preparation of residents of therapeutic specialties at the Department of Hospital Therapy. The purpose of holding a clinical conference of residents is to improve professional and universal competencies and develop clinical thinking in future therapists in the process of teaching hospital therapy. The authors consider the clinical conference as an effective form of educational process that combines students' independent activities, interaction with the teacher, and the formation of basic skills for future medical practice.