ОБРАЩЕНИЕ К ЧИТАТЕЛЯМ
REVIEWS
Many prognostic tools have been developed over the past decades, however, the identification of biomarkers that can predict the risk of acute coronary disease and its associated complications, especially heart failure, remains a promising direction, the study of which will provide understanding of the pathophysiology of this disease and identify new targets for therapy. One such potential biomarker is soluble suppression of tumorigenicity 2, which is able not only to predict left ventricular remodeling and poor clinical outcome among patients with acute coronary syndrome, but also to complement other well-established cardiac biomarkers such as natriuretic peptides and cardiac troponins. At the same time, if a number of separate but often converging pathways are involved in the pathogenesis of acute coronary disease, then multimarker approaches with various combinations of new cardiac biomarkers and their continuous assessment are likely to improve the prediction of cardiac risk and long-term outcomes.
The article presents data on the frequency of the combination of osteoarthritis and cardiovascular diseases, the features of their relationship, the possible impact of cardiovascular diseases and ongoing therapy on the development and progression of osteoarthritis.
The review highlights the prevalence, pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of bronchial asthma (BA), comorbid with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Difficulties in diagnosing triggers of extraesophageal symptoms were noted. Based on a large number of clinical studies, the review assesses the possibilities of minimally invasive methods for detecting biomarkers of gastroesophageal reflux (GER) and duodenogastroesophageal reflux (DGER) in the oral fluid. With syntropy of GERD and BA, a significant role and relationship between the parameters of respiratory oxidative inflammation and impaired functions of external respiration was noted. To confirm the reflux origin of extraesophageal respiratory symptoms, it is important to use minimally invasive methods for detecting bilirubin and pepsin in the oral fluid, and to assess the activity of respiratory stress, the determination of its substrates in the blood. Further studies aimed at determining the normative concentrations of DGER substrates in the oral fluid and markers of oxidative respiratory inflammation in the blood will help improve the diagnosis and treatment of BA and GERD syntropy in outpatient practice.
Ischemic stroke (IS) remains the most common neurological pathology [1,2] and can manifest itself in the form of malignant ischemic stroke (MIS), leading not only to severe disability of the patient, but to life-threatening conditions [3,4]. Malignant ischemic stroke is one of the most formidable manifestations of ischemic stroke, threatening disability of the working population and the likelihood of death without the appointment of timely therapy. Diagnosis:“Malignant ischemic stroke” can occur no earlier than 12-24 hours, during which time irreversible changes in the brain may occur, accompanied by its pronounced edema, with the threat of subsequent herniation, therefore, the appointment of adequate and timely therapy is necessary as soon as possible [5,6] . Taking into account the peculiarities of the course of the disease, there is a need to search for predictors of MIS. In order to timely predict irreversible consequences, in the above literature review, we consider modern approaches to diagnosing the malignant course of ischemic stroke. The analysis of the literature data allows us to determine some clinical and laboratory predictors of the development of malignant ischemic stroke and methods for assessing the severity of ischemic stroke. Various possibilities of using the studied markers for the purpose of practical use in the early diagnosis of MIS are considered. Based on the literature data, the possibilities of diagnostics were analyzed in order to prescribe timely and adequate therapy before the onset of irreversible changes in the brain.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Aim. To evaluate whether the history of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in patients undergone cardiac surgery (coronary artery bypass grafting - CABG) causes alterations in their clinical and laboratory status.
Materials and methods. Clinical data of 42 patients undergone CABG in 2019 were analyzed. Informed written consent was obtained from all participants in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Determination of COVID-19 positive or negative status was performed due to results of nasal and throat swabs using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) or positive serum COVID-19 antibodies. Statistical analyses were performed using Jamovi software.
Results. In COVID-19 positive patients compared to COVID-19 negative patients: the level of serum cholesterol was significantly higher: 5,22 [4,03; 6,22] vs. 4.06 [3,56; 4,88] mmol/L, р = 0,005; OR 0,492 [0,282; 0,858] 95% CI, p ratio 0,012; the level of low-density lipoproteins was significantly higher: 3,27 [2,16; 3,96] vs. 2,28 [1,60; 3,08] mmol/L, p 0,014; OR 0,518 [0,294; 0,914] 95% CI, p ratio 0,023; the incidence of chronic kidney disease stage C3a (CKD) was higher: 7 (16,7%) vs. 1 (2,4%), p 0,008; OR 0,0779 [0,00855; 0,710] 95% CI, p ratio 0,024; tendency to a higher serum creatinine: 89,7 [83,0; 105,0] vs. 81,0 [75,0; 90,5] μmol/L, p 0,060; OR 0,976 [0,945; 1,01] 95% CI, p ratio 0,153; tendency to a lower glomerular filtration rate using CKD-EPI: 66,1 ± 17,3 vs. 75,7 ± 16,1 ml/min/1,73m2, p 0,034; OR 1,0368 [0,9962; 1,08] 95% CI, p ratio 0,076; tendency to a higher serum D-dimer level: 154 [104; 364] vs. 137 [97; 173] ng/ml, p 0,07; OR 0,997 [0,994; 1,0] 95% CI, p ratio 0,141; tendency to a higher mean heart rate 75 [71; 79,5] vs. 72 [63; 74,5] bpm, p 0,026; PR 0,951 [0,886; 1,02] 95% CI, p ratio 0,169. Heart rate variability parameters haven’t shown statistical significance between groups.
Conclusion. Patients with a history of COVID-19 who underwent CABG had alterations in their clinical and laboratory status. These alterations should be thoroughly investigated to make a forehanded change in their therapy.
Objective: to study the level of type 1 vascular endothelial adhesion molecule in patients with coronary heart disease depending on the stage of chronic kidney disease. Material and methods: the study included 115 patients, mean age was 67.56±12.42 years (63 men, 52 women) with ischemic heart disease (CAD), stable angina (tension), functional class 1–3, chronic kidney disease (CKD) C1–C3. The level of the vascular endothelial adhesion molecule type 1 (VCAM 1) was assessed using the enzyme immunoassay kit for the quantitative determination of human VCAM 1 ThermoFisher scientific. Results: in patients with CAD and CKD, the level of serum VCAM 1 progressively increases as angina pectoris worsens and can be regarded as an early marker of CAD progression. The level of VCAM 1 does not depend on the stage of CKD. When studying the correlation relationships between the level of serum VCAM 1 and clinical and laboratory data, it was found that there is a correlation relationship between VCAM 1 and the level of SBP and DBP. Conclusion: in patients with CAD and CKD, it is advisable to use the determination of the level of VCAM 1 to identify patients with a high risk of cardiovascular complications.
Objective: to study the clinical characteristics of patients with the phenotype of obese brochial asthma in combination with chronic coronary heart disease. Material and methods: in an open-label clinical trial, two groups of patients with chronic coronary heart disease (CHD) and bronchial asthma (BA) were formed. Patients of group I (n=43) had obesity as a concomitant disease. Group II (n=50) were non-obese patients. All patients underwent a general clinical examination. The results of Holter’s daily monitoring of the electrocardiogram (HMECG), duplex scanning of the brachiocephalic arteries (BCA DS), transthoracic echocardiography (EchoCG), coronaroangiography (CAG), and spirography were evaluated. The results of biochemical blood testing were also evaluated. Results: for patients of group I, the main complaints were shortness of breath (84% vs 62%, p=0,036) and cough (65% vs 40%, p=0,027) compared with patients of the control group. According to the results of echo-CG in this group, signs of overload of the left heart were revealed. The LV EDV score was more significant than in the control group (p=0,034). The thickness of IVS is also more significant in patients of group I (p=0,022). Ultrasound of the common carotid and internal carotid arteries revealed atherosclerotic plaques in 53% of patients of group I vs 30% (p=0,037) of the control group. According to CAG, the prevalence of RCA stenosis was more significant in patients of group I (56% vs 24%, p=0,003). In patients of group I, spirometry showed a more pronounced decrease in OFV1 (64,1±6,7 vs 66,9±7,1, p=0,042). Conclusion: the adipose BA phenotype combined with CHD is characterized by more frequent cough complaints as the equivalent of choking in bronchobstructive syndrome. Also, patients are more likely to note shortness of breath as the equivalent of angina pain and, possibly, the manifestation of respiratory and heart failure. These clinical features of the phenotype are reflected in the results of instrumental examination methods: pronounced atherosclerotic vascular damage, signs of overload of the left heart, a more significant decrease in the FEV1 rate.
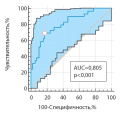
Objective:to establish predictors of failure of dual antihypertensive therapy in patients with arterial hypertension (AH) of high and very high cardiovascular risk, to create a predicting model for the negative outcome of dual antihypertensive therapy. Materials and methods: The study included 88 patients with uncontrolled hypertension who did not receive basic antihypertensive therapy, mean age 58.0±1.52 years. The examination was carried out on the basis of the current regulatory documents regulating the examination at the stationary stage. Additionally, the level of highly sensitive C-reactive protein and blood uric acid was determined. 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) and electrocardiogram (ECG), respiratory polygraphy of sleep, and computerized capillaroscopy were performed. The search for predictors and the creation of a predictive model were carried out using the binary logistic regression method. Results: the effectiveness of dual drug therapy was 33.0%. Prognostic markers associated with a negative outcome of treatment were identified: interventricular septal thickness (IVS) (OR 3.44; p=0.009), linear density of the capillary network (OR 4.65, p<0.001), area density of the capillary network (OR 3, 98; p<0.001); remodeling coefficient (OR 8.40; p=0.003), mean nighttime systolic blood pressure (SBP) (OR 1.94; p=0.014), mean daily SBP (OR 2.86; p=0.014), SDNNi (OR 2 .86; p=0.007). The final model included the IVS, areal density of the capillary network, and the average daily SBP. Model characteristics: regression coefficient 25.74; p<0.001; p Wald 0.049; OR 9.1 (95% CI 3.12; 26.82). The sensitivity of the method was 83.1%, the specificity was 69.0%. The area under the ROC curve was 0.805±0.05 (95% CI 0.707; 0.882). The cut-off point corresponded to the calculated probability value of 0.599. Conclusions: the study demonstrated the low efficacy of dual antihypertensive therapy. Given the lack of approved algorithms for predicting outcomes of drug treatment in patients with uncontrolled hypertension, the developed model is of clinical interest and may be useful in achieving better BP control. To improve the quality of the model in order to increase the sensitivity and specificity of the method, further study on larger samples is required.
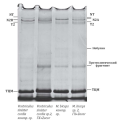
Objective: to conduct a comparative analysis of the dynamics of changes in the end products of glycolysis and the isoform composition of the giant protein - titin and nebulin in the skeletal and cardiac muscles of animals with HC during long-term administration of simvastatin. Materials and methods: the study was conducted on rats that were kept on a high-fat and high-carbohydrate diet for three months. After GC confirmation, the animals were divided into groups: group 1 received only the experimental diet; group 2 received simvastatin in the form of an aqueous suspension for two months at the rate of 0.012 g/kg of animal weight once a day. The control group of animals was kept on the general diet of the vivarium. Results: The formation of HCh was accompanied by the accumulation of pyruvate and lactic acid both in the myocardium and in muscle tissue. The revealed metabolic changes reflect structural disorders and indicate the formation of hypoxia. Against the background of the introduction of simvastatin, both in the myocardium and in the skeletal muscles, a decrease in the level of pyruvate and lactic acid was noted and these indicators approached the values of the control group. Such changes reflect a tendency to restore the integration of intracellular metabolic processes. However, in the study of titin and nebulin proteins against the background of the use of simvastatin, both in the myocardium and in skeletal muscles, structural changes were noted: accumulation of the proteolytic T-fragment, a decrease in the content of intact titin isoforms. Also, statin-induced structural abnormalities have been identified in earlier studies of rat muscle biopsies. Conclusion: The conducted comparative study clearly demonstrates that the myocardium, along with skeletal muscles, is the target organ of the toxic effect of statins. Based on this, the data obtained as a result of the study, it is important to take into account the pharmacotherapy with statins.
Objective: to study the features of coronary calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease receiving renal replacement therapy with program hemodialysis. Materials and methods: in the process of an open clinical trial, a group of patients (n = 43) with end-stage chronic kidney disease (23 women and 20 men) was formed. The average age of patients was 54±13 years, the median length of dialysis therapy was 11 [6; 16] months. All patients received renal replacement therapy with program hemodialysis. The procedures were carried out on artificial kidney devices according to the standard scheme 3 times a week for 4 hours. Patients underwent traditional clinical and laboratory examination. All patients were assessed for coronary calcification by multispiral computed tomography. On the Agatston scale, the severity of coronary calcification was assessed taking into account the density and area of calcium deposition. Results: on the results of multispiral computed tomography to determine the degree of calcification of the coronary arteries, we found that 48% of patients had low and minimal calcification, 16% — insignificant calcification, 36% — measured and pronounced calcification. When comparing laboratory parameters in the groups of patients with different calcification of the coronary arteries, the level of inorganic phosphorus (1,64±0,07 mmol/L) was significantly higher in patients with insignificant, moderate and severe calcification than in patients with minimal and low calcinosis (1,35±0,12 mmol/L) (p=0.04). There was a pronounced direct correlation between age and calcium index (r=0,52, p=0,0011). With an increase in dialysis experience, an increase in calcium index is noted (r = 0,14; p = 0,045). Conclusion: in 52% of patients with end-stage chronic kidney disease receiving renal replacement therapy with program hemodialysis, coronary calcification is determined from the results of multispiral computed tomography of the coronary arteries. Patients with moderate to severe coronary calcinosis have significantly higher levels of serum phosphorus compared to patients with minimal to low calcinosis. At the same time, the age of patients and the length of dialysis therapy affect the severity of coronary calcinosis
Objective: to study the immune mechanisms of inflammation of the patients with BA in association with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM). Materials and methods: the study involved 215 patients with persistent BA of moderate severity at the age of (28.6±2.4) years, including 88 men (40.9%), 127 women (59.1%). Among the examined patients with BA there were 64 — group I, persons with BA in association with type 2 diabetes — 151 (group II), in whom, along with routine laboratory and instrumental methods, cellular immunity, IgE and lymphocytic autoantibodies were determined. Results: patients with BA in combination with type 2 diabetes more often have an uncontrolled course of the disease with a complication in the form of grade II respiratory failure. In patients with BA, as well as with BA in combination with type 2 diabetes, the formation of secondary immunodeficiency due to the cellular link was noted. The combination of BA and type 2 diabetes is characterized by the most pronounced negative changes in cellular immunity among all examined patients. In BA in combination with type 2 diabetes, a decrease in the concentration of IgE was noted along with an increase in the number of lymphocytic autontibodies. Conclusion: patients with BA in combination with type 2 diabetes have a more severe course of BA and the addition of a more destructive autoimmune to allergic inflammation, which increases the risk of complications of both diseases.
Objective: to study of the features of the spread of anxiety syndrome in patients with chronic non-communicable diseases (CNCD) in outpatient practice. Materials and methods: the study included persons of both sexes over 18 years of age who visited outpatient facilities in a large industrial center of Eastern Siberia in the summer of 2022. Diagnosis of chronic NCDs was established according to modern clinical guidelines. The examined were divided into two groups. The first group included persons without NCDs, the second group included patients with concomitant NCDs. The psycho-emotional state was assessed using the Spielberger-Khanin test with separate determination of the levels of personal and situational anxiety. Statistical data analysis was carried out using the Statistica 12.0 software package (StatSoft Inc., USA). Results: the level of situational anxiety in patients with chronic NCDs was statistically significantly higher compared to individuals without concomitant somatic pathology. In patients with chronic NCD, compared with individuals without them, a significant increase in the median scores for the level of low and moderately expressed personal anxiety and for the level of moderate and high situational anxiety was revealed. In the group of patients with CND, a high level of personal and situational anxiety was significantly more often observed in comparison with persons without CND. Conclusion: the prevalence of anxiety syndrome, especially situational anxiety in patients with chronic NCD in the outpatient network is quite high and reaches 93%, which requires a solution to the issue of practical psychiatric care for these patients.
Objective: to assess the subchronic toxicity of bis(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)dimethyltin (Me-3) and (3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)triphenyltin (Me-5) with the identification of external signs of toxicity and changes in the indicators of the functional state of the liver and kidneys of Wistar rats (females) with 14-fold daily intragastric injection to simulate a metronomic chemotherapy regimen. Materials and method: the study was conducted on 24 Wistar rats (females) weighing 190-210 g. The tested compounds were administered fourteen times daily intragastrically at a total dose of 2000 mg/kg for Me-3, 954 mg/kg for Me-5. Results: for substances belonging to the class of organic tin derivatives: the features of the toxic process and indicators of the functional state of detoxification organs (liver and kidneys) with subchronic administration were revealed. The injection in total doses amounting to a half-year dose with a fourteen-fold administration did not cause the death of animals and the development of external signs of toxicity, changes in the functional state of the liver and kidneys were not noted. Conclusion: the analysis of the results of the study will allow us to develop optimal schemes for the injection of organotin compounds containing a fragment of 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol in the metronomic regimen.
CLINICAL CASES
Pheochromocytoma (PC) is a tumor of chromaffin cells of the sympathetic-adrenal system that produces a large amount of catecholamines (adrenaline, norepinephrine, dopamine). There are no reliable data in the literature on the frequency of cardiac manifestations of pheochromocytoma, which is associated with the rarity of this pathology. This case demonstrates the development of catecholamine-induced cardiomyopathy, proceeding under the guise of a heart attack, as the primary manifestation of pheochromocytoma. The patient was referred with a diagnosis of «Ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction» to perform coronary angiography, according to the result of the study, no pathology of the coronary arteries was detected. In the process of additional examination, a pheochromocytoma of the left adrenal gland was revealed. The initial changes in the electrocardiogram, echocardiographic examination, and laboratory parameters regressed, which confirmed the development of cardiomyopathy that developed against the background of pheochromocytoma. Currently, there is an increasing amount of information about non-ischemic myocardial damage in patients with pheochromocytoma. These changes in the form of clinical manifestations (pain behind the sternum, shortness of breath, various types of arrhythmias) as well as non-specific changes according to ECG data, disturbances of local kinetics with a decrease in global myocardial contractility without stenotic damage to the coronary artery were called catecholamine-induced cardiomyopathy.
Currently, there is an increase in the number of publications, devoted to the problem of multiple primary tumors — neoplasms that occur simultaneously (synchronously) or alternately (metachronously), developing independently and independently of each other within the same or different organs. They are described as two, three or more nosologies. Due to the presence of defects in the immune system in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, solid tumors of different localization are a common finding. Their development is possible in other hematological diseases. This is probably due to success in the cure of tumor diseases, an increase in the life expectancy of patients, urbanization, an increase in the intensity of carcinogenic technogenic and medicinal effects, the presence of primary and secondary immunodeficiencies, as well as the use of modern diagnostic methods. Simultaneous detection of myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative diseases in a patient is rare (in 1%), and this entails difficulties in diagnosing and prescribing therapy with such an association. In this regard, alertness is necessary in the presence of clinical and laboratory signs of a disease of the blood system that are not characteristic of the established type of hemoblastosis. And, of course, of undoubted interest is our own experience in managing such patients.
HISTORY OVERVIEW
The Imperial University of Warsaw can rightfully be considered the progenitor of the Rostov State Medical University. At the origins of the formation of the Department of Hospital Therapy in Warsaw was an experienced internist and progressive scientist Andreev Nikolay Agapievich (1836-1883) - pathologist and therapist, corresponding member of the Imperial Vilna Medical Society, Active State Councillor, doctor of medicine, professor, head of the department from 1870 to 1875. This article is dedicated to his blessed memory and to the 140th anniversary of the death of one of the founding fathers of the Hospital Therapy Department of RostSMU.