REVIEWS
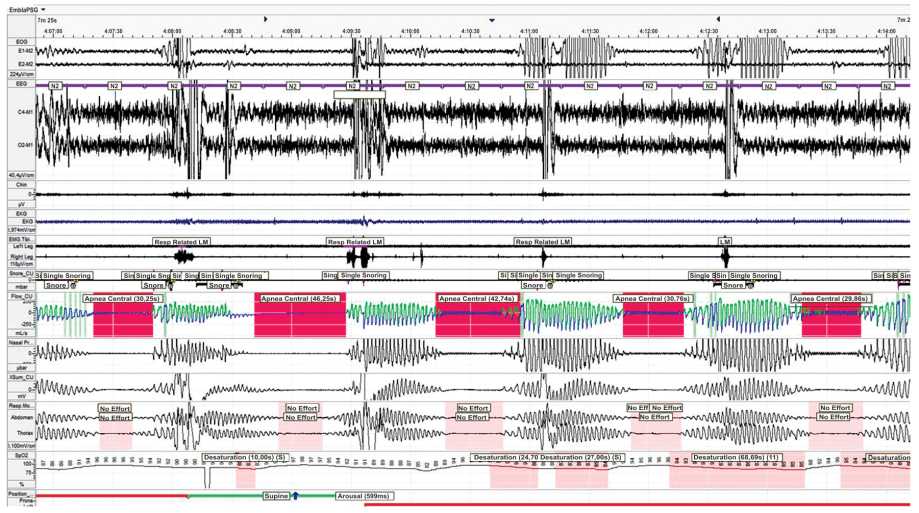
The risk factors, clinical manifestations, pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment options for central sleep apnea and Cheyne-Stokes respiration in patients with heart failure are highlighted in this review. The effectiveness and prospects of therapeutic approaches are discussed: CPAP therapy, adaptive servo ventilation, transvenous stimulation of the phrenic nerve.
The increasing prevalence of overweight and obesity is a public health problem worldwide. During the COVID-19 pandemic, obesity is associated with a higher risk of severe disease and adverse clinical outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection. It may be associated with chronic systemic inflammation, impaired immune response and metabolic disturbances in obese patients. In order to establish possible pathogenetic links between obesity and COVID-19, an analysis of experimental, clinical studies, their meta-analyzes, literature reviews from the PubMed/MedLine database was carried out using the keywords «COVID-19» and «obesity». This review discusses the potential pathogenesis and treatment features of obese patients with COVID-19.
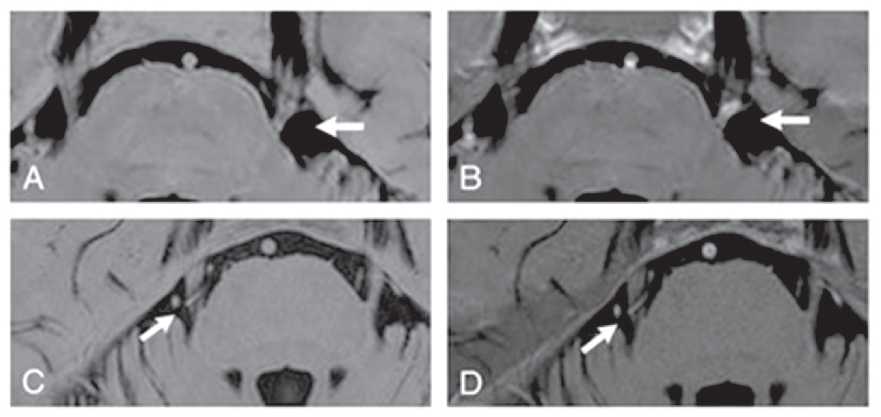
The thematic review discusses various points of view on the topographic and atomic features of the location of the root of the trigeminal nerve and the superior cerebellar artery that serve as the foundation for the development of classical trigeminal neuralgia. The diagnostic capabilities of magnetic resonance imaging in the recognition of neurovascular conflict as the pathogenetic basis of the disease are considered. The search for diagnostic criteria that distinguish neurovascular conflict from neurovascular contact by improving both the performance of MRI and the new technical possibilities of its interpretation is highlighted in the chronological aspect. The possibilities of multispiral X-ray computed angiography in 3D mode as an alternative method for diagnosing neurovascular conflict are described.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Objective: To study the association of beta-adrenergic reactivity index of erythrocyte membranes with polymorphisms of the beta-1-adrenergic receptor gene ADRB1 (Ser49Gly and Arg389Gly).
Material and methods: the study included 62 patients with myocardial infarction (MI) — 49 men (median age of 58.0 (47.5; 64.5) years) and 13 women (median age of 76.0 (61.5; 81.0) years). All patients underwent analysis of beta-adrenoreactivity of erythrocyte membranes using the BETA-ARM AGAT reagent kit within the first 6 hours from the onset of MI. The patients were divided into 2 groups depending on the value of the beta-adrenergic reactivity index (β-ARM). The first group (n = 11) included patients with a normal P-ARM level (from 2 to 20 conventional units). The second group (n = 51) consisted of patients with increased values of β-ARM (more than 20 standard units). Genetic analysis for the determination of ADRB1 gene polymorphisms (Ser49Gly and Arg389Gly) was carried out by isolating DNA from peripheral blood leukocytes (Wizard Genomic DNA Purification Kit) with PCR amplification and further electrophoretic detection. Statistical processing of the obtained data was carried out using Statistica 10 software and the demo version of IBM SPSS Statistics 20.0.
Results: patients with elevated β-APM values were characterized by higher levels of myocardial necrosis markers in the blood (CPK, CPK-MB, and troponin I) in acute myocardial infarction than for patients of the first group (p = 0.009, p = 0.032 and p = 0.001, respectively). In addition, the second group of patients was characterized by a more frequent development of acute left ventricular failure (33.3%, p = 0.026), as well as a history of arterial hypertension before the development of index MI (90.2%, p = 0.044). With regard to the Arg389Gly polymorphism, significant differences were found among patients with normal and increased P-APM values in the acute period of MI. Thus, the second group of patients consisted mainly of carriers of the 1165CC genotype of the ADRB1 gene (n = 29, 56.9%, p = 0.043). The carriage of the 1165G allele was much more often observed among patients of the first group (81.8%; OR = 5.93; CI 1.16-30.25; p = 0.043).
Conclusion: an association of the 1165CC genotype of the Arg389Gly polymorphism of the ADRB1 gene with increased β-APM values in acute MI was established. The detected associations may indicate a possible genetic predisposition to SAS hyperactivation, and also indicate the need for further study of polymorphisms and the level of expression of the ADRB1 gene in patients with high individual values of β-APM established in the acute period of MI.
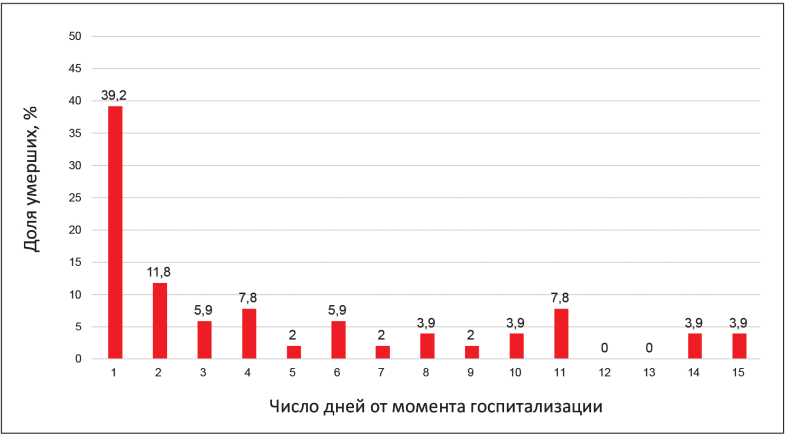
Objective: to analyze the leading causes of early (first two days) and late (after the second day) hospital mortality among of patients with acute decompensated heart failure.
Materials and methods: a retrospective single-center cohort (n=718) of patients with acute decompensated heart failure.
Results: predictors of prognosis for early hospital mortality were pulmonary edema, hepatomegaly, the need for inotropic and vasopressive drugs, the level of systolic blood pressure and creatinine. Predictors of prognosis for late hospital mortality were pulmonary edema, the need for inotropic drugs, community-acquired pneumonia, and laboratory markers of acute renal injury.
Conclusion: Tactical approaches are proposed to reduce hospital mortality of patients with acute decompensated heart failure.
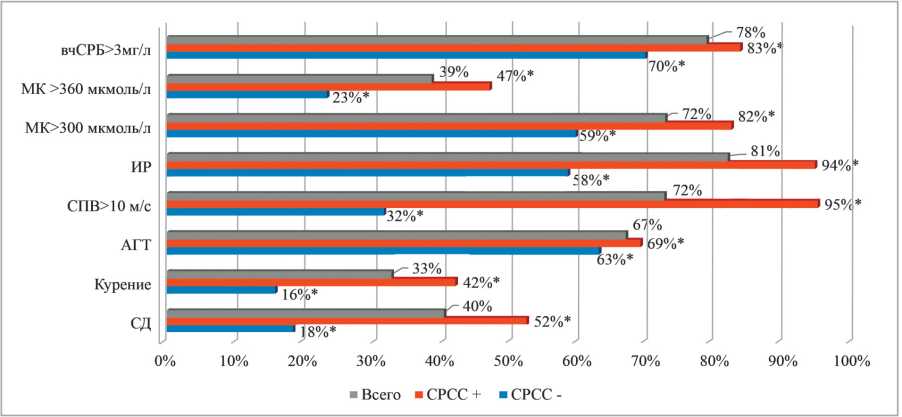
Purpose: identifying the causes of early vascular aging (EVA) in patients with metabolic syndrome (MetS), assessing the relationship between vascular age and various metabolic disorders, the severity of metabolic syndrome , tissue and circulating risk markers, the severity of non-infectious inflammation, and derive a new score for calculation vascular age and predicting early vascular aging in patients with metabolic syndrome.
Materials and methods: а total of 750 patients aged 35 to 80 years with metabolic syndrome were examined. Early vascular aging syndrome was detected in 484 patients with metabolic syndrome and carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV) values exceeding expected for average age values by 2 or more SD.
Results: Multiple logistic regression shown, that presence of type 2 diabetes and IR were associated with greater risk of early vascular aging, the risk of having early vascular aging increased by 76% with an increase in HOMA-IR by 1 unit, by 17% with an increase in carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity by 1 mg/l, by 4% with an increase in DBP by 1 mm Hg, and by 1% with each 1 pmol / L increase in the level of UA. For vascular age, calculated from carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity, SCORE scale, QRISK-3 scale and Framingham scale, respectively. Diabetes mellitus and clinical markers of IR (yes/no), HOMA-IR and UA level were used to develop a new VAmets score for EVA prediction providing a total accuracy of 0.830 (95% CI 0,799 to 0,860).
Conclusion: parallel efforts for effective integration simple clinical score into clinical practice have been offered. Our score (VAmets) may accurately identify patients with metabolic syndrome and early vascular aging on the basis of widely available clinical variables and classic cardiovascular risk factors can prioritize using of vascular age in routine care.
Aim: to assess the awareness of doctors about the main provisions of the European and Russian clinical guidelines for the management of patients with dyslipidemia and arterial hypertension (AH).
Material and methods. Anonymous survey of 584 physicians and cardiologists of Krasnodar and Krasnodar Territory was carried out. The questionnaire contained 9 multiple-choice questions.
Results: according to the results of the questionnaire, 1/3 of doctors knew the target values of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in very high-risk patients. If the target level of LDL cholesterol was not achieved on an adequate dose of statin, 75.1% of colleagues would not have added ezetimibe. For hypertriglyceridemia in patients receiving an adequate dose of statins, 47% of physicians would prescribe treatment that does not comply with clinical guidelines. More than half of the doctors gave correct answers to the questions about antihypertensive therapy. However, the target level of blood pressure was incorrectly indicated by 47.3% of respondents, 71.6% of colleagues made a mistake with the tactics of starting therapy, and 51.5% of doctors incorrectly assessed the situation with the prescription of a triple fixed combination of drugs.
Conclusion: а significant part of practicing doctors (therapists and cardiologists) were not sufficiently informed about the main provisions of the new recommendations and were guided by old (outdated) ideas.
Objective: to reveal the features of the use of beta-blockers (BB) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and chronic heart failure (CHF) in real clinical practice.
Materials and methods: the study included 90 patients with COPD and CHF, and 41 patients with CHF of ischemic genesis without COPD.
Results: patients with COPD and CHF were significantly less likely to receive beta-blockers (BB) compared with patients with CHF. Of the BB patients with COPD and CHF were primarily prescribed bisoprolol, its average dose was 4.45 ± 1.74 mg per day. Patients with COPD and CHF of ischemic genesis of BB were prescribed significantly more often, and diuretics were significantly less likely than patients with COPD and CHF without myocardial infarction. Patients with COPD and CHF with ejection fraction of the left ventricle (LVEF) more than 40% were less likely to take BB than patients with COPD and CHF with reduced EF (less than 40%), and also less frequently, than patients with CHF without COPD with LVEF more than 40%.
Conclusion: BB, as first-line drugs in the treatment of CHF, was prescribed on an outpatient basis only to half of patients with COPD and CHF, which does not comply with current guidelines for the management of patients with comorbid conditions. In the vast majority of cases, highly selective BB were prescribed. It should be noted low doses of BB, the absence of dose titration, which does not correspond to modern recommendations for the treatment of chronic heart failure.
Objective: of the research was to study preclinical changes in heart rate variability (HRV) associated with overweight and obesity in young people in order to determine the targets of predictive therapy.
Material and methods: the study involved 105 young men and 111 young women aged 18 to 30 years. Questionnaires, anthropometry with determination of body mass index and waist circumference, bioimpedansometry with determination of body fat (BF) and visceral fat (VF) level, as well as monitoring of HRV based on short (ten-minute) records were carried out.
Result: young people of both sexes showed a high frequency of overweight (24.1%) and obesity (18.5%), as well as a low level of physical activity (FA, 46.3%). In 28.8% of young men and 12.5% of young women with overweight and obesity, there was a high level of VF. Taking into account the outstripping increase in VF as compared to BF, it is reasonable to divide the VF levels into low (<5 conventional units), intermediate (5-9 conventional units), and high (> 9 conventional units). In overweight young people, compared with normal body weight, HRV is characterized by less pronounced parasympathetic activity, and in girls compared with young men, there is less total HRV. A high HRV level is associated with such HRV indicators as an increase values of LF/ HF and SDANN, reflecting, respectively, a reduction in the parasympathetic and enhanced sympathetic activity of the autonomic nervous system with a predominance of the central circuit of heart rhythm regulation over the autonomous one.
Conclusion: to diagnose autonomic imbalance in young people, it is necessary to determine the composition of the body, FA level, take into account the individual dynamics of HRV parameters, since they rarely exceed the norm. Changes in total HRV, sympathetic and parasympathetic activity during the non-drug correction of obesity should be monitored with an emphasis on pNN (50) and SDANN indicators associated with BF, and when correcting physical activity — on the indicator of voltage index of regulatory systems.
Purpose: tto assess the possibility and feasibility of using virtual technologies to reduce the intensity of pain in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in real clinical practice.
Materials and methods: we observed for 2 weeks 48 women with rheumatoid arthritis verified by modern methods during inpatient treatment at the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution of the Research Institute-KKB No. 1 n.a. prof. S.V. Ochapovsky. The patients were divided into two groups according to the case-control principle, of which 1 out of 28 patients constituted the intervention group, and 2 out of 20 patients were observed as controls. The study included only women from 20 to 75 years old, signed informed consent. According to clinical data and indicators of the course of rheumatoid arthritis, the groups were comparable. The severity of pain manifestations of the articular syndrome, quality of life, and duration of pain during the day were analyzed. All patients received comparable standard basic therapy. Patients of the 1st group were additionally conducted daily 20-minute lessons according to the method of "distracted involvement" using virtual games through VR-glasses.
Results: the using of computer games with VR glasses led to a decrease in the severity of pain by 29,62% in patients of group 1 versus 18,97% in the comparison group. They had a significant decrease in intense pain 3 days earlier and by the end of the course of virtual therapy they recorded a significant (by 37.5%) reduction in the duration of pain during the day (with a 26% effect in the comparison group). A positive aspect of the use of virtual technologies was the reduction in the total dose of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs taken in the observation group by 48% (versus 26% in group II). This fact creates conditions for reducing the drug load in the total volume of therapy and prevents the development of side and unwanted iatrogenic reactions.
Conclusion: the application of the method of "distracted involvement" with the use of games through VR-glasses in patients with rheumatoid arthritis is an effective method of analgesic non-drug action in complex therapy. The low cost and high analgesic efficacy of the method makes it possible to recommend its use in the inpatient treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. At the same time, a number of issues of safety and effective duration of course use of virtual games in order to reduce the severity of pain syndromes require further study.
Purpose: to study the relationship of the indicators of the general blood test with the severity of the course of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients.
Materials and methods: the study included 165 patients (92 men — 55.8%, and 73 women — 44.2%, the average age — 59.9 years) who were treated at the Moscow State University Medical Center in the period from April to June 2020 with a diagnosis of COVID-19. All patients underwent: general blood test, CRP, CT of the lungs. The severity of the clinical condition was assessed using the SHOCK-COVID and NEWS-2 scales.
Results: a more severe clinical condition of patients and a greater severity of lung damage on admission were statistically significantly associated with a decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin, as well as with a greater width of the distribution of red blood cells (RDW-SD). The rate of erythrocyte sedimentation (ESR) was significantly associated with the clinical condition of patients evaluated by SHOCK-COVID (r=0.61, p<0.001) and the marker of CRP inflammation (r=0.55, p<0.001). An increase in the absolute number of neutrophils (N), a decrease in the absolute number of lymphocytes (L), and, as a result, an increase in the N/L ratio index was a marker of a more severe course of the disease. It was the N/L index that had the maximum correlation coefficient with the most commonly used marker of systemic inflammation - CRP (r=0.50, p<0.001). The decrease in the level of CRP by discharge was associated with a significant decrease in ESR (r=0.36, p<0.001), the index of the ratio of neutrophil and lymphocyte levels (N/L) (r=0.39, p<0.001), and an increase in the width of the distribution of red blood cells (RDW-SD r=0.25, p<0.01; RDW-CV r=0.57, p<0.001).
Conclusions: the most informative indicators of the general blood test at admission to the hospital, allowing to assess the severity of the disease — the width of the distribution of red blood cells, the index of the ratio of neutrophils to lymphocytes and ESR.
Purpose: to study the factors that affect the indicators of humoral immunity in medical students and doctors of the city of Simferopol by means of questionnaires and serological testing. The data obtained may indicate a fairly high involvement of medical students and medical workers in the processes of formation of population immunity to COVID-19.
Materials and methods: from 14.09.20 to 06.10.20 the 67 students, as well as 19 doctors and nurses living in the Republic of Crimea have been examined by the method of enzyme immunoassay to detect IgG serum antibodies to the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. All the examined subjects completed the online questionnaire.
Results: According to the ELISA the antibodies to CoV-19 were detected in 14 students (20,9% [18,3%; 25,1%]), as well as in 6 health workers (31,6% [28,9%; 34,2%]) of the total examined number. The survey revealed a number of adverse factors that contribute to the depletion of the body's immune reserves in both students and medical professionals.
Conclusion: the studies of the seroprevalence to the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus in various population groups, as well as the mechanisms and features of seroconversion, the kinetics of the immune response and the intensity of humoral immunity may possess an extremely important role in developing the strategy and tactics of antipandemic measures and in the future COVID-19 vaccine prophylaxis.
CLINICAL CASES
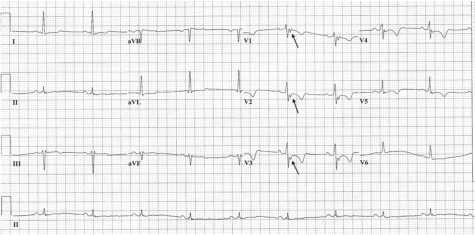
Arhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ADP) refers to hereditary myocardial diseases, in which there are structural and functional disorders in the right ventricular myocardium, causing rhythm and conduction disorders, including fatal ventricular arrhythmias. ADP is considered one of the most common causes of sudden cardiac death in young people and people who are engaged in sports. However, in practice, there are cases of this disease in people of an older age category. Diagnosis of ADP is still difficult due to the possible long-term asymptomatic course of the disease. The article describes a clinical case of ADP in a 48-year-old man.
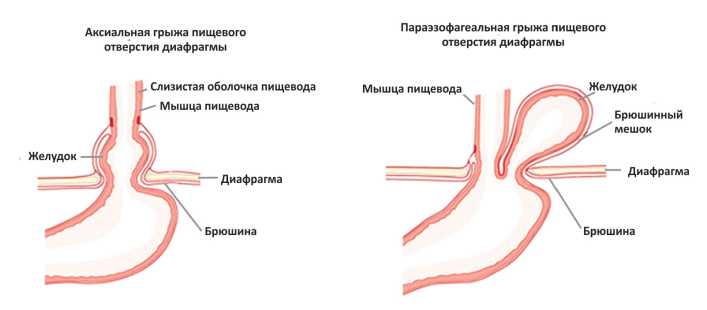
A hernia of the esophageal aperture of the diaphragm is considered as one of the factors contributing to the development of gastroesophageal reflux disease and requires a complete and comprehensive examination of the patient. Routine esophagogastroduodenoscopy does not give a complete picture of the disease, and therefore patients receive symptomatic treatment for a long time. Paraesophageal hernia of the esophageal aperture of the diaphragm are not well understood yet due to their relatively low frequency of occurrence, may be asymptomatic or manifest as chest pain of noncardiac origin. A patient with a long history of gastroesophageal reflux disease associated with a giant paraesophageal hernia of the esophageal aperture of the diaphragm is presented as a clinical case.