“South Russian Journal of Therapeutic Practice” is a medical journal of scientific and practical orientation, intended for therapists, researchers, hospital physicians and post-graduate students of medical universities, who are interested in the latest achievements of contemporary medicine of internal diseases.
The main focus of the journal is national and international recommendations, reviews, lectures, original works on therapy, cardiology, pulmonology, gastroenterology, nephrology and other therapeutic disciplines, as well as description and analysis of the clinical cases, difficult for diagnostics, and the legal aspects of medical practice. Among the authors are the leading scientists from the research and educational institutions of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Southern Federal District and other regions of Russia, as well as young researchers and practicing physicians. Well-known scientists and clinicians, including seven Academicians of the Russian Academy of Sciences, four Corresponding members of the Russian Academy of Sciences, four Chief experts of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, and six Chief experts of the Southern Federal District are the members of the journal editorial board and editorial council.
The journal publishes articles on the following subject areas:
- 01/14/00 - clinical medicine:
- 01/14/02 - Endocrinology
- 01/14/04 - Internal diseases
- 01/14/05 - Cardiology
- 01/14/11 - Nervous diseases
- 01/14/21 - Hematology and blood transfusion
- 01/14/22 - Rheumatology
- 01/14/25 - Pulmonology
- 01/14/28 - Gastroenterology
- 01/14/29 - Nephrology
02.14.00 - preventive medicine:
- 02/14/02 - Epidemiology
- 02/14/03 - Public health and healthcare
03/14/00 - biomedical sciences:
- 03/14/06 - Pharmacology, clinical pharmacology
12.00.00 - Jurisprudence:
- 12.00.05 - Labor law; social security law
Current issue
REVIEWS
Cardiovascular, kidney, and metabolic diseases are pathophysiologically interconnected, generally forming a serious problem for health care worldwide, associated with a significant increase in morbidity and mortality. In 2023, the American Heart Association presented the cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome (CKMS), in which dysfunction of one organ leads to progressive deterioration of the condition of others, proposed a classification and an integrated approach to the management of patients with this complex pathology. In recent years, the arsenal of drugs for the treatment of patients with CKMS has significantly expanded due to successful studies of several drugs with different mechanisms of action and approved indications for use. The review summarizes data from new literature sources, briefly describes the pathophysiology, classification, and effective methods of treatment of CKMS at all stages of its development. Patient-oriented modern medical care can improve the quality of life and prognosis in CKMS.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Objective: to investigate the prevalence and clinical features of aortic dissection in patients presenting with neurological symptoms. To evaluate the characteristics of the disease course and diagnosis depending on the presence of pain syndrome.
Materials and methods: a retrospective cohort comparative study was conducted using the medical records of 130 patients hospitalized in the State Budgetary Healthcare Institution “Research Institute – Regional Clinical Hospital No. 1 n. a. prof. S.V. Ochapovsky” with a diagnosis of Stanford type A aortic dissection from 2020 to 2024. Patients with aortic dissection and
neurological symptoms were divided into two groups: those with and without pain syndrome. A comparative analysis of risk factors, clinical manifestations, diagnostic data, treatment strategies, and outcomes was performed in both groups, with an assessment of the statistical significance of identified differences.
Results: all patients had Stanford type A dissection; DeBakey type I was identified in 84 (65 %) patients, and type II in 46 (35 %). Among the 130 patients, 31 (23.8 %) presented with neurological symptoms. In 11 (35 %) of these, the typical pain syndrome was absent. Mortality among patients with neurological manifestations was 71 % (22 out of 31). Comparative analysis showed that a higher frequency of diagnostic errors was observed in the group of patients with neurological symptoms but without pain syndrome (p = 0.02). In this group, there were significantly more women (72.7 % vs. 25 %, p = 0.05), ischemic stroke developed more frequently (36.4 % vs. 5 %, p = 0.02), and a diagnosis of aortic dissection was significantly less often established during life – in 36.4 % of cases, it was confirmed only at autopsy (vs. 5 %, p = 0.02). Patients with neurological symptoms and typical pain demonstrated a higher frequency of hypotension, likely related to more severe vascular disturbances. A clinical case of a painless variant of aortic dissection, manifested by impaired consciousness and monoparesis of the arm, is presented.
Conclusion: aortic dissection, especially in the presence of neurological symptoms, presents a diagnostic challenge requiring a careful approach to atypical manifestations, such as ischemic stroke. The absence of pain syndrome can complicate diagnosis and delay the initiation of treatment. The
obtained data require further research to improve diagnostic strategies, especially in cases with atypical presentations.
Objective: to evaluate the presence and characteristics of left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction (DDА) in various phenotypic variants of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) based on Doppler echocardiography (EchoCG).
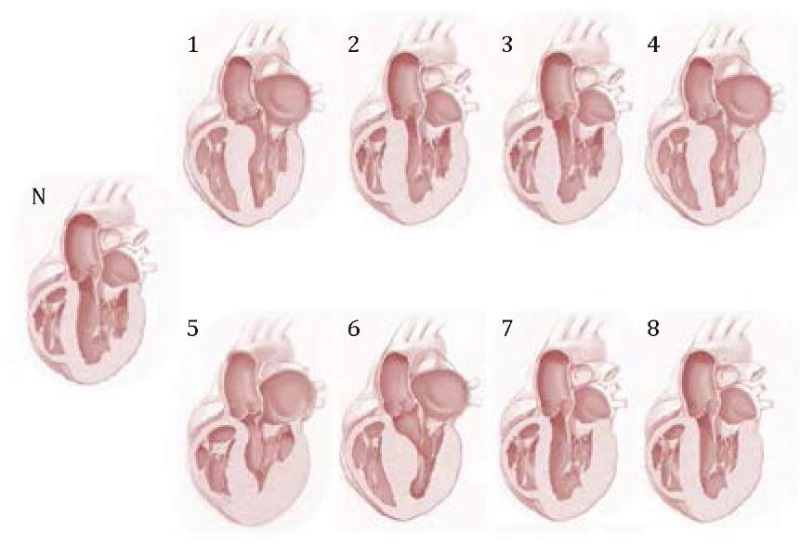
Materials and methods: a total of 305 patients with HCM aged 18-88 years (mean age 60.6 ± 11 years) were examined, including 189 (62 %) men and 116 (38 %) women. The diagnosis was established based on two-dimensional EchoCG data upon detection of LV myocardial hypertrophy in the absence of any other pathological process responsible for the severity of such hypertrophy. The control group consisted of 50 practically healthy individuals comparable in gender and age. The severity, localization and extent of hypertrophy, transmitral blood flow parameters, size and volume of the left atrium were assessed. Depending on the predominant localization of hypertrophy, all patients were divided into 8 morphological groups according to the recommendations for HCM of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation 2020. An analysis and comparison of the parameters of diastolic function was carried out depending on the HCM phenotype.
Results: 305 patients with HCM were divided into 8 typical groups: 128 patients in group 1 (hypertrophy of the basal part of the interventricular septum, IVS), 45 — in group 2 (hypertrophy of the entire IVS, “neutral septum”), 50 — in group 3 (IVS hypertrophy of “reverse curve”), 11 — in group 4 (combined hypertrophy of the IVS and other parts of the left or right ventricle), 7 — in group 5 (apical hypertrophy with or without involvement of other LV segments), 11 — in group 6 (midventricular IVS hypertrophy with LV free wall hypertrophy), 12 — in group 7 (LV free wall hypertrophy), and 41 — in group 8 (symmetrical or concentric LV hypertrophy). Among all patients, DDF was detected in 286 (93.8 %) of cases. The most frequently recorded DDF type I (impaired relaxation) was in 196 (64.3 %) patients, type II (pseudonormalization) — in 64 (21%) and type III (restrictive type) — in 26 (8.5 %). In the control group, DDF type I was recorded in 8 (16 %) patients, type II — in 6 (12 %) and type III in none of the cases. Despite the noted variations in the frequency of detection of one or another type of DDF in the phenotypic groups, statistical analysis did not reveal any significant differences.
Conclusion: diastolic function disorders were detected in the overwhelming majority of patients with HCM: in 93.8 % of cases. The spectrum of DDF in this disease is wide and includes all types of diastolic abnormalities. In patients with HCM, impaired relaxation (DDF type I) is detected in 64.3 % of patients, pseudonormalization (II) — in 21 % and restrictive type (III) — in 8.5%. Analysis of the dependence of the frequency of registration of the noted types of DDF depending on any hypertrophy phenotype did not show significant differences.
Objective: to evaluate the effect of sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) on survival and the course of the early postoperative period during myocardial revascularization using coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Materials and methods: an analysis of previous oral hypoglycemic therapy was performed in patients with type 2 DM who underwent CABG (from June 1, 2024 to December 31, 2024) at the Krasnodar Research Institute of Cardiology and Cardiology No. 1. During the analyzed period, myocardial revascularization by CABG was performed in 458 patients, of whom 119 suffered from T2DM. The latter were divided into groups depending on the previous oral hypoglycemic therapy: group 1 — patients who took at least 3 months before CABG and sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 — 30 people; group 2 — patients who took other hypoglycemic therapy before CABG — 89 people.
Results: group 1 was statistically significantly younger (mean age 62.83 ± 9.01 versus 67.40 ± 4.88, p = 0.018). Of the concomitant pathologies in group 1, low functional class of heart failure predominated (I and II according to NYHA: 66.67 % versus 53.33 %, p = 0.038). Laboratory data of group 1 were better in glomerular filtration rate (86.05 ± 15.16 ml/min versus 72.03 ± 15.97 ml/min, p < 0.001) and more favorable lipid profile (total cholesterol 3.59 ± 0.90 mmol/l versus 4.18 ± 1.11 mmol/l, p = 0.027). In group 1, clinically insignificant ketonuria (0.5-1.5 mmol/l) without metabolic acidosis was detected in 4 patients in the early postoperative period. In the early postoperative period, complications were less common in group 1 (46.67 % versus 73.33 % in group 2, p = 0.035), which, however, did not affect the length of hospital stay (10.80 ± 3.88 days in group 1 and 11.20 ± 4.60 in group 2, respectively, p = 0.717) and in-hospital mortality (mortality was 0 % in both groups).
Conclusions: this study demonstrates a reduction in a number of early postoperative complications, probably due to anti-inflammatory and positive cardiorenometabolic effects, and a decrease in left ventricular volume overload on the background of iNGLT-2. It is noteworthy that not a single case of euglycemic ketoacidosis in the postoperative period has been reported, despite the fact that “major surgeries” such as CABG are considered to be at high risk of developing EKA against the background of the use of drugs of this group in patients with DM2. In addition, a more favorable lipid profile and glomerular filtration rate during iNGLT-2 therapy may have advantages in terms of long-term prognosis, which must be confirmed or refuted in large samples of patients with an assessment of long-term outcomes and postoperative outcomes.
Objective: based on the data from the total register of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) in the Krasnodar Territory, identify the factors associated with reduced LV EF in patients with primary acute myocardial infarction (MI).
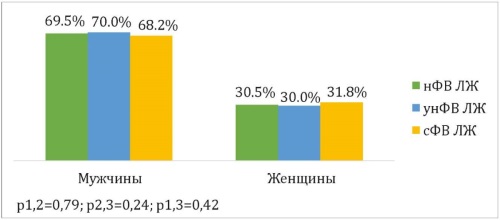
Materials and methods: a retrospective study was conducted on 5,655 patients with primary MI included in the total ACS registry in the Krasnodar Territory from 2022 to 2024. The study examined the relationship between LV EF and the clinical, anamnestic, and diagnostic data of the patients. LV EF values were assessed using the Simpson method before discharge from the hospital or earlier in case of hospital-acquired death. Depending on the LV EF, all patients were divided into groups with low (≤ 40 %) LV EF (n = 1125), moderately low (41-49 %) LV EF (n = 1258), and preserved (≥ 50 %) LV EF (n = 3272).
Results: the data of 5,655 patients included in the total ACS registry in the Krasnodar Territory for the period from 2022 to 2024 were analyzed. Factors such as a history of smoking, chronic kidney disease, hypertension, and peripheral atherosclerosis, increased troponin, creatinine > 130 mmol/l, and glucose > 15 mmol/l upon admission according to laboratory blood tests, and ST segment elevation and the formation of a pathological Q wave on an electrocardiogram, as well as acute heart failure (AHF) of class II–IV according to Killip and the presence of early complications of MI were identified as predictors of a decrease in LVEF in patients with primary MI.
Conclusions: presence of smoking, chronic kidney disease, arterial hypertension and peripheral atherosclerosis in the anamnesis, increase in troponin, creatinine > 130 μmol/L and glucose > 15 mmol/L, ST segment elevation, formation of pathological Q-wave, the phenomena of OSN II–IV class according to Killip, and the presence of early complications are associated with a decrease in LV EF in patients with MI.
Objective: to study the incidence and performe the features of anemia in patients with axial (axSpA) and peripheral spondyloarthritis (perSpA).
Material and methods: 112 patients with axSpA and 34 patients with perSpA were included in the study. The median age was 39 [33; 47] years, the proportion of men was 71 (60.2 %) patients. The BASDAI and ASDAS-CRP scores were calculated, the hemogram, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), the level of C-reactive protein (CRP), and ferrokinetic parameters were studied. Depending on the indicators of iron metabolism and CRP levels, anemia of inflammation (AI), iron deficiency anemia (IDA) or a combination of both (AI + IDA) were diagnosed.
Results: anemia was detected in 53.6 % of patients with axSpA, in 47.1 % of patients with perSpA (p = 0.506). In most cases, AI with or without an iron deficiency component was recorded in axSpA and perSpA — 83.7 % and 87.5 %, respectively (p = 0.409). A mild anemia corresponded in 93.3 % of patients with axSpA and in 81.3 % of patients with perSpA (p = 0.250). In both groups, the presence of anemia was associated with increased levels of CRP and ESR.
Conclusion: anemia is a common hematological disorder in patients with spondyloarthritis, reflecting the high inflammatory activity of the basic inflammatory process. The incidence, severity, and type of anemia in patients with axSpA and perSpA are comparable.
Objective: to investigate the immune status of patients with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) and GERD.
Materials and Methods: 136 patients were observed, including 100 patients with САP at an average age of (42.3 ± 2.9) years, including 34 patients with САP combined with GERD NERD (group I), 66 patients with САP without of GERD (group II), 36 patients with GERD without CAP observed on an outpatient basis, Group III. The control group consisted of 34 practically healthy donors. Diagnosis of CAP and GERD was carried out in accordance with the existing recommendations. The examined patients had the state of indicators of cellular and humoral immunity and phagocytic activity of monocytes in the dynamics of treatment.
Results: patients with CAP combined with GERD and dyspepsia symptoms have a higher level of systemic inflammation than patients with CAP without GERD. The course of CAP combined with GERD is accompanied by secondary immune deficiency due to cellular and humoral immunity, with an imbalance in the phagocytic activity of monocytes. Laboratory signs of systemic inflammation and immune disorders are not fully resolved during the clinical recovery of patients.
Conclusions: the identified changes create the preconditions for a personalized approach to the treatment of such patients, with the possible addition of drugs with anti-inflammatory and immunocorrective effects to reduce the likelihood of early and late complications of both comorbid diseases.
Objective: to conduct a comparative assessment of cardiometabolic risk factors, anxiety and depression among students of primary and senior courses of medical university and medical college.
Materials and methods: the study involved 281 students of the 1st year, 169 students of the 6th year of the medical university, as well as 166 students of junior courses and 98 students of senior courses of the medical college. A questionnaire was conducted among the respondents to identify cardiometabolic risk factors, a physical examination with an assessment of body weight, height, body mass index and blood pressure. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) was used to assess the level of anxiety and depression. Statistical processing of the material was carried out using the SPSS 20.0 program.
Results: it was found that among students of the 1st year of the medical university, compared with students of the initial courses of the medical college, unhealthy diet and anxiety at the subclinical level are statistically significantly lower, the average systolic blood pressure is lower, and the prevalence of low physical activity, excessive salt intake, smoking and alcohol consumption is higher. When comparing senior students, smoking, alcohol consumption, excessive salt in the diet and unhealthy diet were statistically significantly less common among university students. In addition, it was found that students of the 1st university year have an increased risk of depression in the presence of anxiety and abdominal obesity. In a group of the 6th university year students, the risk of anxiety and depression increases with excessive salt intake, decreases with excessive sugar intake. At the same time, an average academic score of ≥ 4.5 significantly reduces the risk of anxiety and depression among students, regardless of the course of study.
Conclusion: the results of the study demonstrate the high importance of studying the prevalence of cardiometabolic risk factors among young people and subsequently developing targeted measures to prevent the occurrence of cardiometabolic diseases among students.
Objective: to analyze vitamin D availability in patients with irritable bowel syndrome of various etiologies.
Materials and methods: 148 patients with irritable bowel syndrome with a predominance of diarrhea were examined. Group I included 88 patients with irritable bowel syndrome after COVID-19; group II included 60 patients in whom the disorder was stress–induced. The control group included 30 relatively healthy subjects. Vitamin D availability was assessed for all participants.
Results: an analysis of vitamin D provision in patients suffering from irritable bowel syndrome showed a predominance of patients with reduced levels of this micronutrient. In both groups of patients with irritable bowel syndrome, the incidence of vitamin D deficiency was significantly higher than in the control group. Thus, in group I, a decrease in serum calcidiol levels was found in 63 (71.6 %) patients, which was statistically significantly (p < 0.001) higher than in the control group, and in group II — in 24 (40.0 %) patients (p < 0.01), where the disorder was induced by stress.
Conclusions: patients with irritable bowel syndrome are characterized by an insufficient supply of vitamin D. At the same time, this imbalance is more typical for patients who have developed IBS against the background of a new coronavirus infection.
Objective: to determine the frequency of associations between polymorphic markers of the AGTR1 (A1166C), AGT (M235T), CYP11B2 (C-344T), ACE (I/D polymorphism) genes and the risk of developing hypotension in patients with newly diagnosed stage 1–2 hypertension after 3 weeks of pharmacotherapy with angiotensin II receptor blockers.
Materials and methods: the study included 179 patients from the Moscow region with newly diagnosed stage 1–2 hypertension and low/moderate cardiovascular risk (CVD), of which 141 (78.8 %) were women and 38 (21.2 %) were men, aged from 32 to 69 years (mean age — 58.2 ± 6.4, median age 60 (57–63 years)). They were randomly assigned to treatment groups with valsartan or irbesartan according to CVD stratification.
Results: no statistically significant association was found between the frequency of hypotension development and the AGTR1 A1166C genotype in patients receiving either irbesartan (p = 0.398) or valsartan (p = 0.179). No statistically significant association was found between the frequency of hypotension development and the AGT C4072T genotype in patients receiving irbesartan (p > 0.999), while the highest frequency of hypotension was observed in CC homozygotes receiving valsartan (p < 0.001). No statistically significant association was found between the frequency of hypotension development and the ACE genotype in patients receiving either irbesartan (p > 0.999) or valsartan (p = 0.149). No statistically significant association was found between the frequency of hypotension development and the CYP11B2 C344T genotype in patients receiving either irbesartan (p = 0.741) or valsartan (p = 0.14).
Conclusion: the study results do not confirm a significant impact of the aforementioned genetic markers on the development of hypotension in response to ARB therapy.
Objective: to evaluate the dynamics of the main symptoms of functional dyspepsia (FD) in patients treated with a drug based on extracts of chamomile flowers, calendula and yarrow herb.
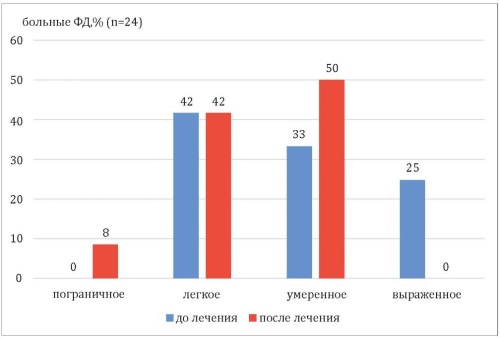
Materials and methods: the study involved 40 patients with mixt clinical manifestations of FD aged from 18 to 53 years: 33 men and 7 women. The patients divided into groups: with a predominance of epigastric pain syndrome (EPS) or with postprandial distress syndrome (PDS). Treatment with a drug based on an alcoholic extract of chamomile flowers, calendula flowers and yarrow herb carried out for 10 days. The effectiveness of treatment assessed using the “7×7” questionnaire. The patient’s quality of life related to his health studied using a visual analogue scale (VAS, EQ-VAS). Psycho-emotional status assessed before the start of treatment using the 4DSQ questionnaire.
Results: after treatment, 79.2 % of patients with EPS and 68.8 % of patients with a prevalence of PDS noted an improvement in their well-being (in dynamics 13 [10.25; 18.75] and 12 [9.25; 15.75] points, p < 0,001), which was expressed in a decrease in the intensity and frequency of pain sensation in the stomach. The number of patients with severe disorders of well-being decreased by 10 times (p = 0.007). The quality of life increased in 57.5 % of the study participants. The improvement in well-being was not associated with the psycho-emotional state of patients before the start of treatment. The dynamics of postprandial disorders was not reliable.
Conclusion: the use of a medicinal product containing extracts of chamomile flowers, calendula and yarrow herbs may be an alternative treatment for pain symptoms in patients with FD.
CLINICAL CASES
The article discusses the signs and diagnostic algorithm of autoinflammatory diseases, principles of therapy. Clinical manifestations and complications of adult-onset Still’s disease are discussed. The most serious complication of this pathology is macrophage activation syndrome. The data of the European clinical guidelines on the principles of treatment of adult-onset Still’s disease and drugs recommended for administration to patients with macrophage activation syndrome are presented. A clinical case of diagnosis of adult-onset Still’s disease in a 36-year-old woman is presented.
Peripartum cardiomyopathy, or Meadow’s cardiomyopathy, is an uncommon but difficult to diagnose disease in the last month of pregnancy or during the five months of the postpartum period. Errors in diagnosis can lead to an incorrect diagnosis and, consequently, to the prescription of inadequate treatment, which is fraught with serious consequences. The presence of a new coronavirus infection can lead to a change in the clinical picture and present certain difficulties for verifying the diagnosis. This clinical case demonstrates the acute development of heart failure against the background of peripartum cardiomyopathy in a patient with a new coronavirus infection. During hospitalization, against the background of characteristic complaints (shortness of breath, shortness of breath, swelling in the legs and pronounced weakness), a cesarean section was successfully performed. Further diagnostics made it possible to establish the diagnosis of peripartum cardiomyopathy.
Since the pathology in question is a diagnosis of exclusion, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis with diseases such as latent idiopathic and familial dilated cardiomyopathies before pregnancy, asymptomatic heart defects, pulmonary embolism. In the treatment of peripartum cardiomyopathy, special attention is paid to the prescription of bromocriptine as the basis of pathogenetic therapy. The presented clinical case demonstrates the importance of timeliness and correctness of diagnostic search in patients with characteristic complaints in the last month of pregnancy or in the postpartum period, complicated by the addition of a new coronavirus infection.
Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis is a rare pathology in the population with polymorphic clinical symptoms and a long history, which makes it difficult to diagnose. The presented clinical case demonstrates the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in the diagnosis of the disease and the high effectiveness of immunosuppressive therapy in relation to all manifestations of the pathology.
HISTORY OVERVIEW
The article presents the life and professional path of a brilliant internist, a passionate scientist, a student of Academician I.P. Pavlov, a representative of the domestic scientific medical therapeutic school — Professor Igor Vladimirovich Zavadsky. His scientific and experimental work devoted to the study of diseases of internal organs, infectious pathology, along with active clinical, pedagogical and social activities made a huge contribution to the development of healthcare first in Kazan and then in Rostov-on-Don, and served as the basis for the formation of a regional therapeutic school. The article is dedicated to the memory of Professor I.V. Zavadsky and is timed to coincide with the 150th anniversary of his birth.