REVIEWS
The review provides information about apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), which is a relatively rare phonotype of HCM. Previously, it was believed that apical HCMP has a favorable prognosis, but recent studies have demonstrated an increased risk of fatal arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death, especially among elderly patients, women and those with comorbidities such as arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus. Patients with apical HCMP complain of chest pain, shortness of breath and palpitations. The diagnosis is based on data from various investigation methods, among which imaging techniques such as echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging are crucial. For apical HCMP, a characteristic sign is the identification of the configuration of the left ventricular cavity at the end of the systole resembling to the type "Ace-of-spades". Treatment includes pharmacotherapy using beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, cardiac myosin inhibitors and surgical interventions. The lack of information on unfavorable prognostic factors, the lack of specific clinical data and the complexity of instrumental diagnosis emphasize the relevance of studying the problem of apical HCMP.
Sexual dysfunction is often associated with hypertension but is not recognized, reported, or adequately treated. Research on sexual dysfunction is sparse, which may be due to the taboo nature of the topic. A literature search was conducted in five databases (PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Cochrane Library and PsycINFO) to identify articles published over the past ten years (from 2014 to 2024), using the keywords “sexual dysfunction”, “arterial” hypertension", "antihypertensive drugs", "erectile dysfunction". The review examines the prevalence, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations of sexual dysfunction in men and women, its relationship with arterial hypertension, antihypertensive therapy, concomitant pathology, and possible methods of correction.
To date, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common chronic liver pathology and already at the stage of steatosis causes a high risk of developing cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Convincing evidence has been obtained that CVD is the most common cause of death in patients with NAFLD. Common risk factors (insulin resistance, abdominal obesity, dyslipidemia, hyperuricemia, chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus) and similar pathophysiological mechanisms (endothelial dysfunction, changes in lipid metabolism, systemic inflammation, plaque formation/instability, oxidative stress) of NAFLD and CVD, allow us to consider NAFLD not only as a key risk factor for the development of CVD, but also as a co-factor in the progression of cardiac pathology. The progression of NAFLD itself leads to a more severe course of CVD.
Among hematological diseases, Multiple myeloma (MM) is the second most common malignancy in adults worldwide. In the vast majority of cases, MM remains incurable, despite improvements in progression-free survival and overall survival due to advances in pharmacotherapy, as well as the emergence of innovative drugs in recent years. Unfortunately, this does not prevent patients from relapse and, ultimately, multidrug resistance and poor prognosis. In conditions of limited funding, one of the determining factors for the success of therapy is the cost of treatment. There is a need to conduct a clinical and economic analysis of the use of targeted drugs to determine the most economically feasible treatment option. The purpose of the review is to provide an overview of current and experimental treatments for relapsed/refractory MM (RRMM), with an emphasis on their pharmacoeconomic availability to assist clinicians in their decision-making process. Let's look at the latest data that will help improve approaches to the treatment of this still incurable disease and analyze pharmacoeconomic studies of modern expensive treatment regimens for RRMM in various countries.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Objective: to evaluate the features of the clinical course, as well as heart rate variability (HRV) during inpatient treatment in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and concomitant newly diagnosed hypothyroidism.
Materials and methods: the study included 133 patients with STEMI aged 40 to 88 years who were admitted to the cardiology department. Depending on the presence of newly diagnosed hypothyroidism syndrome, all patients were divided into 3 groups: group 1 consisted of patients with STEMI without hypothyroidism syndrome (n=57), group 2A — patients with STeMI and subclinical hypothyroidism (n=42) and group 2B — patients with STeMI and manifest hypothyroidism (n=34). Clinical symptoms and complications in the acute period of MI were evaluated in all patients, and Holter ECG monitoring (XM ECG) was performed.
Results: during hospital treatment, patients with concomitant manifest hypothyroidism showed more frequent development of cardiac arrhythmias such as paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) (p<0.05), supraventricular extrasystole (NE), paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (LVT) (p<0,05). When assessing the risk of early complications in the acute period of MI, higher scores were recorded in patients with manifest hypothyroidism (p<0.05). The analysis of HRV indicators showed that in the studied patients with concomitant manifest hypothyroidism, despite the presence of an acute period of MI, activation of the parasympathetic link of the ANS (autonomic nervous system) prevails in the regulation of heart rhythm, unlike in patients of the control group and the group with subclinical hypothyroidism, in whom, on the contrary, the influence of the sympathetic link of the ANS prevails.
Conclusion: during hospitalization, patients with manifest hypothyroidism were statistically significantly more likely to develop supraventricular cardiac arrhythmias, and a higher risk of cardiovascular complications in the acute period of MI was determined compared with both the control group and the group of patients with subclinical hypothyroidism. In patients with concomitant manifest hypothyroidism, the activation of the parasympathetic link of the ANS in the regulation of heart rhythm is more pronounced, in contrast to patients in the control group and the group with subclinical hypothyroidism, in whom, on the contrary, the influence of the sympathetic link of the ANS prevails.
Objective: to study the frequency of adherence to therapy, as well as options for existing polypharmacy in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) according to local registry data.
Materials and methods: the study included 398 patients with CHF aged 72.17±11.12 years. Patients were divided into groups depending on the type of polypharmacy (appropriate and inappropriate) according to the criteria of the EURO-FORTA (EF) system (2021) and based on national clinical guidelines (CR) (2020), without polypharmacy (taking 1–4 drugs during prehospital stage) who did not take therapy at the prehospital stage - during the last 3 months before the actual hospitalization.
Results: depending on the type of polypharmacy at the outpatient stage, the analysis was carried out by comparing 4 groups: appropriate (n=103 (EF) and n=120 (CR)) and inappropriate (n=103 (EF) and n=86 (CR) polypharmacy, without polypharmacy (taking 1-4 drugs) (n=91 (EF) and n=117 (KR)) and not taking therapy at the prehospital stage (n=55 (EF) and n=75 (KR)) during the last 3 months before current hospitalization. According to the Morisky-Green questionnaire, 38.44% were adherent to treatment at the prehospital stage, possibly adherent — 7.28%, non-adherent — 54.28%. The lowest quality of pharmacotherapy at the prehospital stage was observed in the group of patients without polypharmacy: they were less likely than patients with appropriate and inappropriate polypharmacy (according to the CR criteria) to take angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) (30.77% versus 55.00% versus 51.16 %, рmg=0.0001), β-adrenergic blockers (β-AB) (52.13% vs. 88.33% vs. 77.90%, рmg=0.0001) and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MCRA) (11.11 % versus 57.50% versus 52.32%, рmg=0.0001) and quite often in 30.77% (p=0.00001) they took potentially unacceptable medications, which further reduced the quality of therapy.
Conclusion: according to the Morisky-Green questionnaire, 54.28% of patients with CHF were non-adherent to therapy at the prehospital stage. Patients with CHF at the prehospital stage in 25.2% did not receive treatment for CHF, in 39.3% there was no polypharmacy and in 69.1% polypharmacy was observed. In multimorbid patients with CHF, polypharmacy had the following advantages: more frequent use of 3-component basic therapy for CHF, more frequent use of ACE inhibitors, β-blockers, AMCR, statins for coronary heart disease (CHD), oral anticoagulants (OAC) for fibrillation/flutter atria (AF/AFL) and antihyperglycemic therapy for diabetes mellitus (DM).
Objective: the effectiveness and safety of endovascular treatment of coronary artery disease in coronary artery disease using various technologies of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was evaluated — implantation of drug-coated metal stents, implantation of bioresorbable stenting scaffolds, the use of drug-coated coronary balloon catheters in the long- term period, 10 years after PCI.
Materials and methods: data obtained from 324 patients with coronary heart disease after PCI using the previously mentioned treatment methods. The endpoint was the loss of the target vessel lumen (TLF), a combination of cardiac death, myocardial infarction, and revascularization associated with the target vessel.
Results: the treatment of patients with coronary heart disease using implantation of drug-coated metal stents, bioresorbable stenting scaffolds or drug-coated coronary balloon catheters is safe and has low rates of cardiac mortality, myocardial infarction and revascularization of the target vessel in the long term. In cases where implantation of stents or scaffolds was contraindicated or impossible due to the small diameter of the artery, diffuse extended lesion and high risk of restenosis, angioplasty with a coronary balloon catheter with an antiproliferative drug coating takes place, showing positive long-term results.
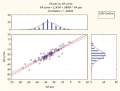
Objective: to compare of 24-hour monitoring and one-time measurement arterial stiffness in patients with bronchial asthma.
Materials and methods: Tthe study included 100 patients with bronchial asthma. All patients underwent 24-hour monitoring and one-time measurement arterial stiffness parameters. At the same time vascular stiffness indicators were examined: pulse wave velocity in the aorta, augmentation index, arterial stiffness index.
Results: Iin the patients with asthma were found to increased 24-hour arterial stiffness. Results of 24-hour monitoring arterial stiffness more than one-time measurement.
Conclusions: 24-hour monitoring arterial stiffness more informative than one-time measurement.
Objective: Cclinical evaluation of the effectiveness and safety of the effect of the regulatory polypeptide drug on neurogenic overactive bladder (OAB) in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS).
Materials and methods: 41 patients with MS and urodynamically confirmed detrusor overactivity were included in a prospective, single-center, simple comparative clinical trial with sequential drug changes. The initial function of the lower urinary tract and its dynamic changes during therapy were studied by filling out a voiding diary and questionnaires using the EDSS, NBSS, SF-Qualiveen, I-QOL questionnaires. The control drug Solifenacin (patient group 1) is a specific competitive antagonist of muscarinic receptors of the M3 subtype, which causes detrusor contraction. The Study Drug (patient group 2) is a complex of regulatory polypeptides that have an organotropic effect on the bladder. Drug administration: control drug for 4 weeks, then an observation period of 4 weeks, after which - taking the Study Drug for 30 days. The results were monitored immediately after the end of taking the Study Drugs, after which they were compared with the initial data. Statistical analysis was carried out by the program “Statistica 10” (StatSoft Inc., USA), using non-parametric data analysis with median analysis, Wilcoxon test and Mann-Whitney U-test search. The results of differences were considered statistically significant if the probability of error was <5% (p<0.05).
Results: Vvoiding diary: 14.6% and 24.4% of patients in groups 1 and 2, respectively, were freed from urinary incontinence; from nocturia —- 31.7% and 56.1% of patients for groups 1 and 2, respectively, the frequency of daily urination was normalized in 53.6% and 70.7% of patients in groups 1 and 2, respectively. NBSS questionnaire: decrease in the total questionnaire score by 29.2% and 47.4% for groups 1 and 2, respectively. SF-Qualiveen questionnaire: an increase in the overall assessment score by 42.3% for group 1 versus +66.5% for group 2. I-QOL questionnaire: improvement in quality of life by 56.0% and 80.4% for groups 1 and 2, respectively. The Study Drug has a higher safety profile compared to Solifenacin.
Conclusion: Tthe effectiveness of the Study Drug in the correction of neurogenic OAB is higher in comparison with Solifenacin, which is reflected in a decrease in urgency, pollakiuria, the number of episodes of urinary incontinence and a significant improvement in the quality of life of these patients. The Study Drug demonstrates a high safety profile in the study.
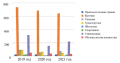
Objective: to study the frequency and structure of traumatic brain injury in the pre-ovoid, covid and post-ovoid periods in Rostov-on-Don.
Materials and methods: to study the frequency and structure of traumatic brain injury in three years from 2019 to 2021 (in the pre-ovoid, covid and post-ovoid periods) according to the neurosurgical department and the department of combined trauma of the Emergency Medical Hospital No. 2 in Rostov-on-Don. Data processing using the IBM SPSS Statictic program version 26.0 using the χ2-Pearson criterion, in pairwise a posteriori comparative analysis, the χ2-Pearson criterion with Yates correction and likelihood correction were used. If the significance level is p<0.05, the differences are statistically significant.
Results: in the pre-crisis period (2019), household trauma prevailed, the total number of hospitalized with TBI was 1,322. Of these, concussions accounted for 71%, brain contusions accounted for 28%, diffuse brain injury — 1%, street injury — 6.9%, transport injury — 6.81% and intentional injury — 24.1%. In the covid period (2020), the total number of patients admitted to the department decreased by 24%. The structure of the injury remained unchanged (concussions in 70% of cases, brain contusions in 28%, diffuse brain injury in 2%). In 2021 (completion of covid restrictions), the number of inpatient patients with TBI remained reduced (by 23%), the ratio of concussions, bruises, diffuse brain injuries remained the same.
Conclusions: during the period of social isolation, there was a decrease in the number of hospitalized with TBI, which coincides with global indicators. The end of the restrictions associated with the pandemic is also characterized by a decrease in the number of patients admitted to the hospital with TBI. At the same time, a decrease in the ratio of the number of hospitalizations to the total number of deaths from head injury in 2019 and 2020 should be taken into account. from 19.83 to 14.98 in the Rostov region (according to the Federal State Statistics Service on the number of deaths from head injuries in 2019-2020), which reflects the level of accessibility of medical care. There was also a significant decrease in household, street, transport, school, sports and intentional types of TBI (p<0.05), while occupational injuries and trauma, the circumstances of which are unknown, did not significantly differ from the pre-pandemic indicators. Taking into account these results will improve the organization of emergency and emergency medical care for patients with TBI.
CLINICAL CASES
Generally pituitary tumors have a benign growth, however, there are difficulties in diagnosis and treatment because of non-specific symptoms and the inability to predict the tumor growth. In clinical practice a hormonal activity of tumors has the significant role. To a greater extent, pituitary adenomas are prolactinomas, but the hypersecretion of prolactin could be combined with an excessive production of somatotropic hormone. In this case, the clinical picture of hyperprolactinemia is accompanied by acromegaly symptoms. The presented clinical case demonstrates the main reasons for the clinical appointment such as menstrual cycle disorders, prenatal preparation. A hyperprolactinemia has been detected, but as a treatment result, drug compensation was achieved and pregnancy occurred, then the woman gave birth without obstetric complications. Subsequently, other complaints arose, which expanded the diagnostic search and revealed the presence of a plurihormonal tumor.
Hepatitis D virus is a dependent virus that depends on hepatitis B virus for replication and transmission. Chronic hepatitis D virus (HDV) is a severe form of viral hepatitis that can lead to end-stage liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver transplantation (LT) is the only treatment option for patients with end-stage liver disease, hepatocellular carcinoma, or fulminant hepatitis caused by HDV coinfection. Also, the presence of a comorbid background is associated with a higher rate of complications, longer hospitalization and worse survival both before and after LT. We present a case of liver cirrhosis as a result of HBV+HDV co-infection in combination with arrhythmia in a patient on the waiting list for LT in the Rostov region.
A case of severe combined damage to the pancreas and liver caused by prolonged alcohol abuse is presented. Acute pancreatitis in the structure of emergency surgical pathology of the abdominal cavity is 25%. The frequency of erroneous diagnostic judgments reaches 35%. In this case, at the beginning, the disease was unequivocally regarded as acute alcoholic hepatitis, which led to a late diagnosis of acute pancreatitis. However, complex conservative therapy proved to be quite effective.
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy is an acquired autoimmune disease of the peripheral nervous system, heterogeneous in course and clinical manifestations, which is curable. The variety of forms of the disease and its course cause difficulties in timely diagnosis and initiation of pathogenetic therapy. This article presents a clinical observation of a patient with a wide range of concomitant pathologies, the presence of which significantly complicated the diagnosis and led to delayed prescription of immunosuppressive therapy.
EXPERIENCE EXCHANGE
The article presents the experience of the staff of the Department of Hospital Therapy conducting a morning conference on the clinical basis of therapeutic departments of a multidisciplinary hospital. The role and importance of the morning conference format in the organization of hospital work in several areas of activity are considered. The role of the conference moderator, the specifics of presenting the material in the reports of the doctor on duty, the possibilities of interdisciplinary discussion of various aspects of diagnosis and treatment in this format were discussed in more detail.