REVIEWS
Hypertension is one of the most common diseases, especially among pregnant women. The combination of hypertension and obesity is a serious problem that requires careful medical monitoring. This literature review highlights the impact of obesity in pregnant women in association with hypertension on the risks of the gestational period and adverse pregnancy outcomes, within the framework of research works by Russian and foreign authors. The search for publications in Russian and English was carried out on the databases and electronic resources PubMed (MEDLIN), Scopus, eLIBRARY using the following keywords: “pregnancy”, “hypertension”, “obesity”. The presented literature review only considers articles with full text in open access. In preparing the literature review, an analysis of publications since 2000 was carried out. Last search date: 01. 27. 2025. A total of 19 articles were reviewed.
The left ventricle is naturally the most vulnerable structure in patients with cardiac pathology — arterial hypertension, coronary heart disease and their frequent combination in clinical practice. The features of its structural and functional disorders are currently well studied and form the basis of pathogenetic therapy. Against this background, the right ventricle has clearly not been studied sufficiently due to the previously existing methodological difficulties in assessing its condition. At the same time, it has been established that dysfunction and remodeling of the right ventricle in patients with cardiac pathology can cause the development of cardiovascular complications, up to fatal. Recently, with the introduction of new ultrasound technologies, the possibilities for assessing the condition of both ventricles in patients with cardiovascular diseases have been expanding, which may in the near future contribute to clarifying their prognosis and improving the effectiveness of therapy.
Autoimmune encephalitides (AIE) are non-infectious immune-mediated inflammatory diseases of the brain parenchyma with frequent lesions of the cortex or deep gray matter with or without involvement of the white matter, meninges, or spinal cord. The most common clinical syndromes of AIE are disorders of the psyche, behavior, cognitive and autonomic functions, movement disorders, as well as epileptic seizures. The diagnosis of AIE can be complicated by the isolated presentation of psychopathological hallucinatory-delusional and emotional-affective symptoms, which can imitate the onset of an idiopathic mental disorder and requires a certain alertness and increased attention to the anamnesis data and assessment of the neurological status. The MRI pattern of limbic encephalitis with unilateral or bilateral involvement of the medial temporal lobes is typical for AIE, however, both normal MRI of the brain and/or spinal cord and involvement of various brain regions in different subtypes of AIE are possible. It is necessary to consider the possibility of not only a recurrent course of AIE, but also the possibility of the overlapping syndromes of AIE and other autoimmune disorders development, including demyelinating diseases – multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders or diseases associated with antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein, which requires longer observation due to the risk of relapse of autoimmune diseases.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Objective: to study the characteristics of cardiorenal relationships in patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) who have suffered a myocardial infarction in combination with CKD.
Materilas and methods: the study included 110 patients with coronary heart disease who had suffered acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in combination with grade 1–2 hypertension, who also had CKD stages 1-3. The clinical study included clarification of the functional class of CHF using a 6-minute walk test (TSH), assessment of the severity of CHF on the SHOKS scale, electrocardiography (ECG), echocardiography (ECHOCG), daily blood pressure monitoring (SMAD), Holter ECG monitoring. The functional state of the kidneys was assessed by the level of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) (formula CKD-EPI), the ratio of albumin to creatinine in daily urine (AU), as well as by the level of N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) in urine.
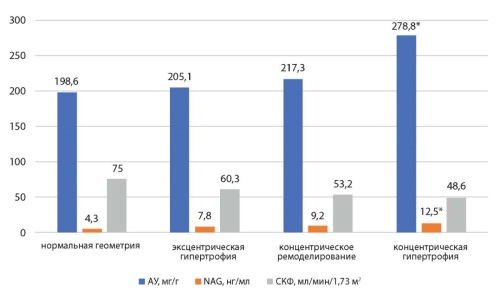
Results: exceeding the level of reference NAG values in urine demonstrated a close association with damage to the epithelium of the proximal tubules. In the studied group, the number of patients with a NAG level of more than 3.16 ng/ml was 96 patients (87.3%). It was shown that the levels of NAG and AU are closely related (r = 0.86, p = 0.001). When analyzing the values of TSH, it was found that as the value of TSH decreased, the level of AU increased (r = 0.34, p < 0.05). It was shown that an increase in the SHOCK score was associated with a decrease in GFR (r = -0.44, p < 0.05). There was no significant correlation between this parameter and AU and NAG in urine. As the left heart dilates, as well as systolic function decreases and myocardial hypertrophy progresses, there is a statistically significant decrease in GFR. It was shown that the values of NAG in urine and AU were higher in a subgroup of patients with concentric hypertrophy. During the analysis of the interrelationships of SMAD indicators and parameters reflecting damage to renal tissue, an increase in the average daily SAD was noted with an increase in the level of NAG in urine and a decrease in GFR. An increase in the level of NAG in urine is also associated with an increase in the variability of SAD, an increase in the index of hypertension time and the rate of morning blood pressure rise. Changes in the values of GFR and AU have fewer connections with the parameters of the SMAD. When analyzing the results of Holter ECG monitoring, it was found that as GFR decreases, the probability of detecting cases of myocardial ischemia (SIM) increases, as well as the duration of all episodes of myocardial ischemia. An increase in the concentration of NAG in urine is associated with an increase in the likelihood of SIM, as well as the duration of episodes of pain-free myocardial ischemia (BBIM).
Conclusions: tubular lesions in the form of an increase in the level of NAG in urine, glomerular lesions in the form of AU and a decrease in the filtration capacity of the kidneys (decrease in GFR) in CKD are associated with the processes of myocardial remodeling in patients with coronary heart disease, PIC and hypertension equally, however, high variability of hypertension, pathological daily profiles of hypertension are more associated with the presence of tubular lesions At the same time , the occurrence of episodes of myocardial ischemia and the duration of pain–free ischemia are associated with the presence of glomerular and tubular lesions.
Objective: to determine whether the features of the performed cardiac surgery influence the development of atrial fibrillation in the early postoperative period.
Materials and methods: the study included patients operated on in the Cardiac Surgery Department No. 2 of the Research Institute — Regional Clinical Hospital No. 1 of Krasnodar in the period from July 1, 2022 to January 1, 2023. During the analyzed period of time, open heart surgery was performed in 552 patients, 60 of whom had postoperative atrial fibrillation (this cohort was called the main group A). Sinus rhythm was recorded in 424 patients, and therefore, using a random number generator, a comparison group (group B) identical in number to the main group was formed, which consisted of 64 patients.
Results: in total, 60 patients (10.9%) developed atrial fibrillation in the
early postoperative period, on average on the 3rd postoperative day (range 1–6 days). Evaluation of the performed surgical intervention showed that patients with postoperative atrial fibrillation more often underwent heart valve replacement surgery or combined prosthetic valve surgery with bypass grafting. If isolated coronary surgery was performed, patients were more likely to tolerate cardiopulmonary bypass, had a longer aortic clamping time, and underwent multivessel bypass with two or more anastomoses.
Conclusion: it is extremely important to find predictors of postoperative atrial fibrillation and, by successfully acting on them, to minimize the likelihood of developing a stroke as a complication of atrial fibrillation, without prolonging the length of stay in the hospital and preventing the burden of such severe consequences of a stroke on the patient’s body and on the healthcare system as a whole, such as severe neurological deficit and disability.
Objective: to perform comprehensive analysis of serum cortisol levels and 24-hour blood pressure profile in male patients with arterial hypertension with or without obesity, and to investigate relationship of blood pressure profile with psychological stress and anxiety levels.
Materials and methods: the study included 76 hypertensive male patients (mean age 46.7 ± 0.5 years). Group 1 included 36 hypertensive men with obesity, group 2 — 40 hypertensive men without obesity. Сontrol group included 26 practically healthy men, comparable in age with groups 1 and 2 (mean age 42.58 ± 1.45 years). All patients underwent 24-hour blood pressure monitoring. Serum cortisol levels was assessed by enzyme immunoassay using Cortisol-IFA-BEST reagent kit. The level of psychological stress was determined by PSM-25 scale. The level of reactive and personal anxiety was determined by Spielberger-Khanin questionnaire.
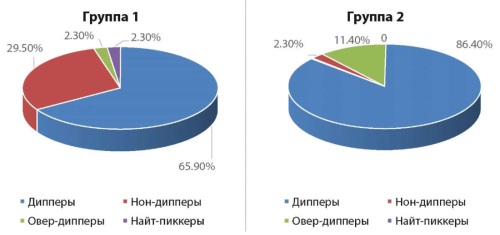
Results: there was a significant increase in average 24-hour, daytime and nighttime blood pressure values, its variability and decline in the nocturnal blood pressure fall (p < 0.05). The highest level of cortisol — 890.2 ± 56.7 nmol / l was detected in group 1 (p < 0.05 compared to group 2 and control group). Correlation analysis revealed significant relationships of blood pressure variability and nocturnal blood pressure fall with the level of anxiety and psychological stress, as well as with cortisol blood levels.
Conclusion: the presence of increased anxiety and psychological stress in patients with hypertension is associated with decline in the nocturnal blood pressure fall and increase in its 24-hour variability, to a greater extent when hypertension is accompanied by obesity.
Objective: to perform a comparative assessment of cardiometabolic parameters and 24-h blood pressure monitoring indicators in pregnant women with white-coat hypertension and normal blood pressure.
Materials and methods: this prospective cohort study included 88 pregnant women aged 18–44 years: group 1 (study group) – 44 women with white coat hypertension (aged 32 ± 5.7 years); group 2 (comparison group) – 44 women with normal blood pressure (aged 28 ± 5.9 years).
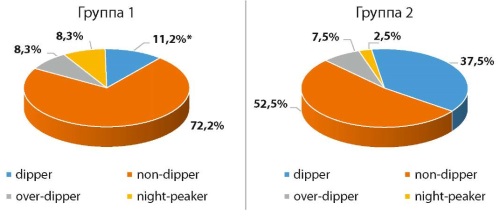
Results: the most significant differences between groups 1 and 2 were observed in serum glucose, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and uric acid. In assessing cardiometabolic risk factors, significant differences were found only in the frequency of abdominal obesity. Only pregnant women with white-coat hypertension had a history of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension. The mean daytime and nighttime systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP), daytime variability of SBP, daytime time index of SBP, daytime and nighttime time index of DBP, daytime mean heart rate, the rate of morning rise of SBP and DBP, as well as a high frequency of non-dippers were significantly higher in pregnant women in group 1 compared to group 2.
Conclusion: 24-h blood pressure monitoring up to 20 weeks of pregnancy allows not only recognition of white-coat hypertension but also identification of a high-risk group for more careful monitoring of pregnant women with this hypertension phenotype.
Objective: to perform a comparative analysis of characteristics of coronary arteries in-stent restenosis and to evaluate effectiveness of repeat revascularization using drug-eluting stents (DES) and drug-eluting balloon angioplasty (DEB) in patients with restenosis depending on the presence/absence of type 2 diabetes.
Materials and methods: the study included 122 patients (age 59.7 ± 4.9 years) treated for in-stent restenosis after primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using bare-metal stents (BMS) and bare-metal carbon-coated stents (BMCCS) for non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome (ACS) at the Republican Clinical Hospital named after N.A. Semashko. Group 1 included 55 patients without a history of diabetes, group 2 included 67 patients with type 2 diabetes. Patients in both groups were divided into 2 subgroups, which underwent repeat revascularization with one of the options - using a new generation DES (stent system with everolimus and sirolimus) or using DEB coated with paclitaxel.
Results: patients in both groups with BMS had a larger length and diameter of in-stent restenosis compared to patients with BMCCS. Patients with diabetes had a significant increase in serum concentrations of endocan, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and C-reactive protein (CRP) compared to patients without diabetes. The following relationships were established during the correlation analysis: group 1 - endocan level with length of restenosis (r = 0.41, p < 0.05), CRP level with length (r = 0.36, p < 0.05) and diameter of restenosis (r = 0.33, p < 0.05); group 2 - endocan level with length (r = 0.51, p < 0.05) and diameter of restenosis (r = 0.54, p < 0.05), PDGF level with diameter of restenosis (r = 0.39, p < 0.05). Twelve months follow-up after repeat revascularization revealed no significant differences in the incidence of major cardiovascular events in group 1 patients with implanted DES and DEB. However, in patients with diabetes, the rate of recurrent restenosis (17.1 %) and stent thrombosis (8.6 %) after revascularization with DES was significantly higher compared to patients with DEB (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: type 2 diabetes significantly worsens the prognosis after PCI, increasing inflammatory and proliferative processes, and appears to be an important modifier of outcomes after repeat revascularization of in-stent restenosis. In patients without type 2 diabetes the use of both DES and DEB for in-stent restenosis demonstrated comparable efficacy and safety during 1-year follow-up. At the same time, in patients with type 2 diabetes DES implantation showed worse results compared to patients with DEB implantation.
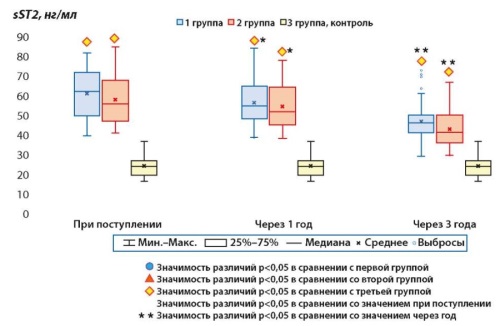
Objective: to study the level of growth stimulating factor (sST-2) in comorbid patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STeMI) who underwent PCI for 36 months.
Materials and methods: the study included 191 people, 36.2 + 1.8 months of follow-up, and included the following stages: I stage (hospital) — from the moment of admission to the hospital for myocardial infarction; II stage (outpatient) — repeated visits 12 and 36 months after discharge from the hospital. The patients were divided into three groups: Group 1 — 69 patients with STEMI + hypertension; Group 2 — 67 patients with STEMI + hypertension + type 2 diabetes; Group 3 (comparison group) — 55 patients with hypertension and DM. Assessment of the plasma level of sST2 was carried out using kits of the company «Critical Diagnostics Presage RST2 Assay kit» (USA). The results were expressed in ng/ml.
Results: the study showed that the level of the sST2 biomarker in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction(STEMI) and type 2 diabetes mellitus(DM2) had no significant differences between the groups. The sST2 values in these patients were significantly higher than in the comparison group. At the stage of hospitalization, the median sST2 in the first group (STEMI and HYPERTENSION) was 62.7 ng/ml, and in the second group (STEMI, hypertension and DM 2) — 56.3 ng / ml. After one year, the median decreased to 55.3 ng/ml and 52.4 ng/ml, respectively, and in the third year — to 46.4 ng/ml and 42.1 ng/ml. Correlations between sST2 values were not found in the acute period and after 12 and 36 months of pregnancy. A moderate association appeared in the 1st and 3rd year of follow-up.
Conclusion: the study revealed that the level of the sST-2 marker in the groups of patients with STEMI\ + AH and STeMI + AH + DM at all stages of the study is comparable and significantly higher than in patients with hypertension + DM. During the study, a correlation was found between the levels of sST-2 outside the acute period of MI. However, there was no significant association between the marker levels at the hospital stage and its values at the end of the study. It was also found that the level of sST\-2 does not depend on the presence of diabetes and is associated with the final systolic, diastolic size and volume of.
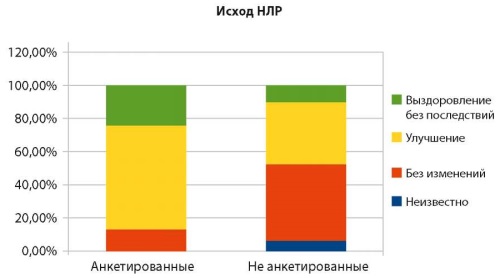
Objective: to analyze the structure of drug prescriptions and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) in the conditions of application of the developed risk-based approach to the audit of pharmacotherapy in patients of outpatient clinics.
Materials and methods: the basis for the study was an outpatient clinic in Rostov-on-Don. The sample consisted of 680 patients observed by a general practitioner. Based on the results of a retrospective analysis of spontaneous reports of ADRs registered in the Rostov region for 2019-2021, a risk-based questionnaire was developed. 50 % (n = 340) of the observed patients were surveyed and, depending on the results, pharmacotherapy was adjusted; the other half of the patients (n = 340) were not questioned and received standard pharmacotherapy. Statistical processing of the results was carried out on a PC using the LibreOffice Calc software package and IBM SPSS Statistics v. 26.
Results: the overall incidence of ADR development in outpatient clinics was 7.5 % (4.5 % and 8.2 %, respectively) (p < 0.05). Patients who underwent a risk-based audit of drug prescriptions had higher rates of the psychological component of health (84.8 ± 3.2 versus 73.2 ± 2.4, respectively) (ρ = 0.386; p = 0.01), the physical component of health (78.3 ± 2.6 versus 69.4 ± 1.8, respectively) (ρ = 0.493; p = 0.01), less drug burden (3.1 ± 1.4 versus 5.3 ± 2.1, respectively) (ρ = 0.452; p = 0.01), the number of unscheduled visits to a therapist (by 24 % on average), the incidence of serious ADRs (by 18 %) (ρ = 0.949; p = 0.01), additional treatment costs (by 23 % on average) (ρ = 0.334; p = 0.01).
Conclusions: the results of the study can be used for further, including pharmacoeconomic studies, to improve the safety of drug therapy, avoid the “cascade of drug prescriptions” and improve the quality of life of specialized patients in outpatient clinics.
CLINICAL CASES
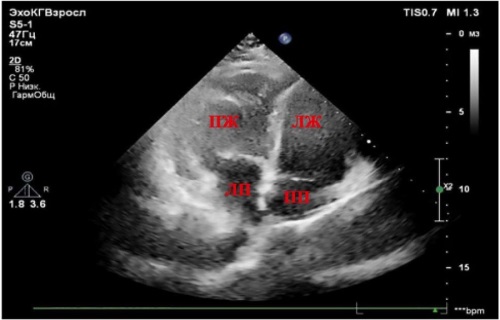
The article examines the transposition of the great arteries, the congenital heart defect, which has a 50 % mortality rate in the first month of life and 90% in the first year. Corrected transposition is one of the types of the pulmonary artery and aorta transposition. The domestic medical literature describes clinical cases of the corrected transposition of the great arteries in pediatrics, detected during the first months and years of life. The article presents the clinical case of the corrected transposition of the great arteries newly diagnosed in adult patient.
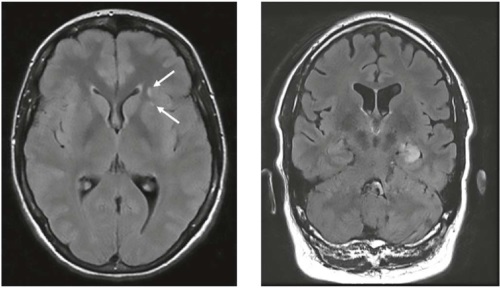
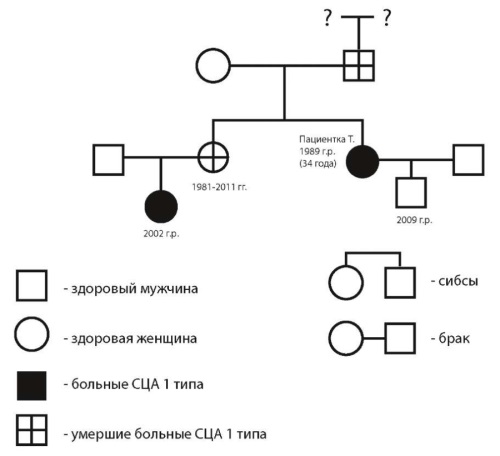
Spinocerebellar ataxia is a neurodegenerative disease with an autosomal dominant type of inheritance, rapid progression of clinical manifestations with onset at a young age. The clinical case of a 34-year-old patient with spinocerebellar ataxia type I, burdened by a hereditary history and the formation of the anticipation phenomenon, is considered. It was noted that
clinical symptoms preceded neuroimaging data.
In recent years, the number of liver transplantations has increased significantly, which determines the urgency of the problem of studying graft dysfunction. A small number of papers have been published on the relationship between the course of ulcerative colitis (UC) and the return of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) after liver transplantation (TP). The article presents a clinical case of the return of PSC after TP against the background of a wave-like course of UC. The clinical picture of the disease and the changes that were revealed during additional examination before and after liver transplantation were discussed.
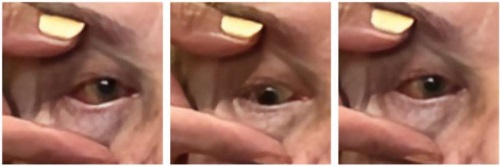
Lymphoproliferative diseases with damage to the organ of vision are quite rare. Such patients may initially consult both ophthalmologists and neurologists, since one of the main symptoms may be ptosis, impaired eye mobility, exophthalmos and diplopia. This article presents our own observation, including a complete clinical, instrumental and morphological analysis of this extremely rare pathological condition.